The Settings page allows you to view and configure various options for the operations system.
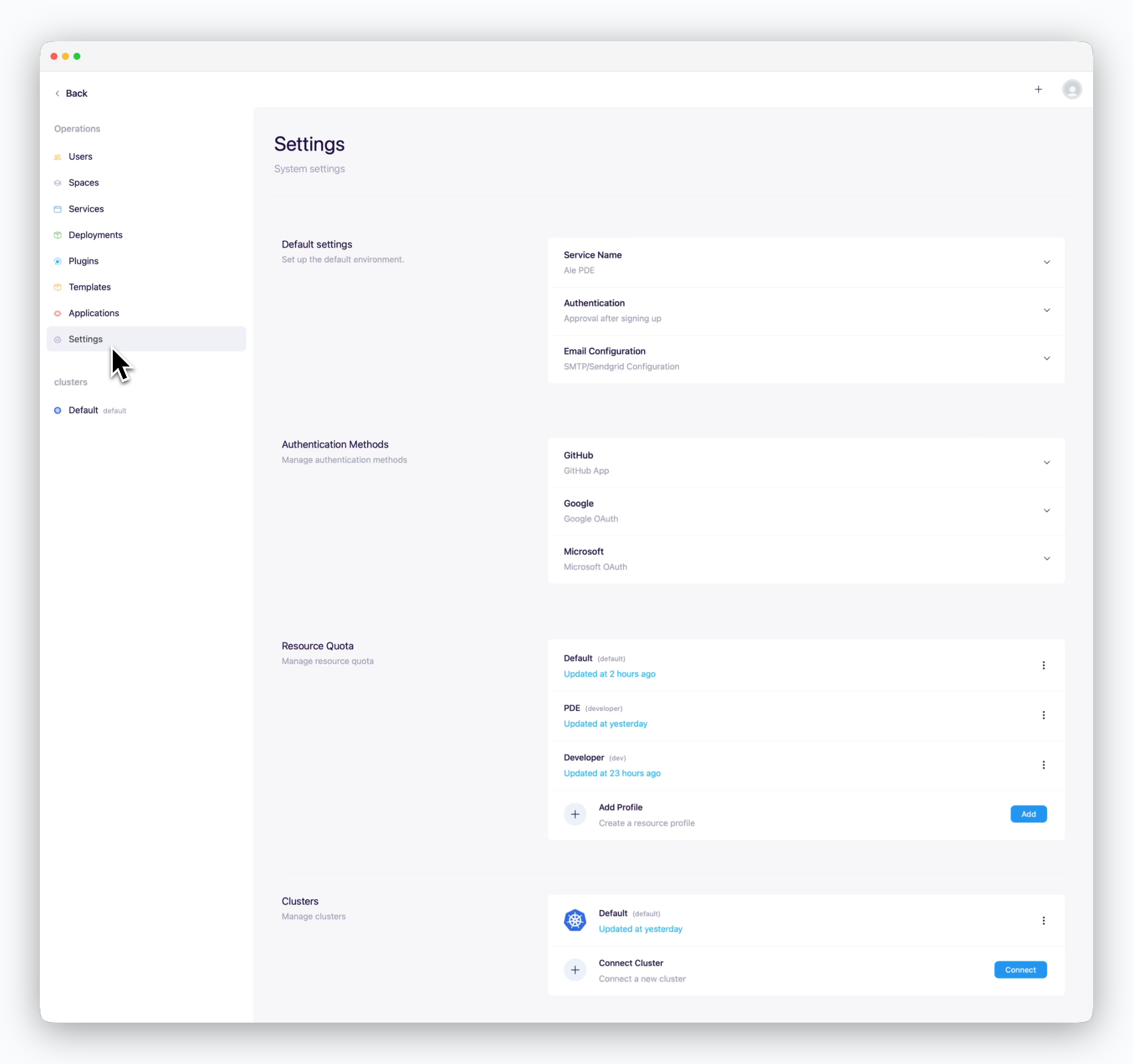
Default Settings
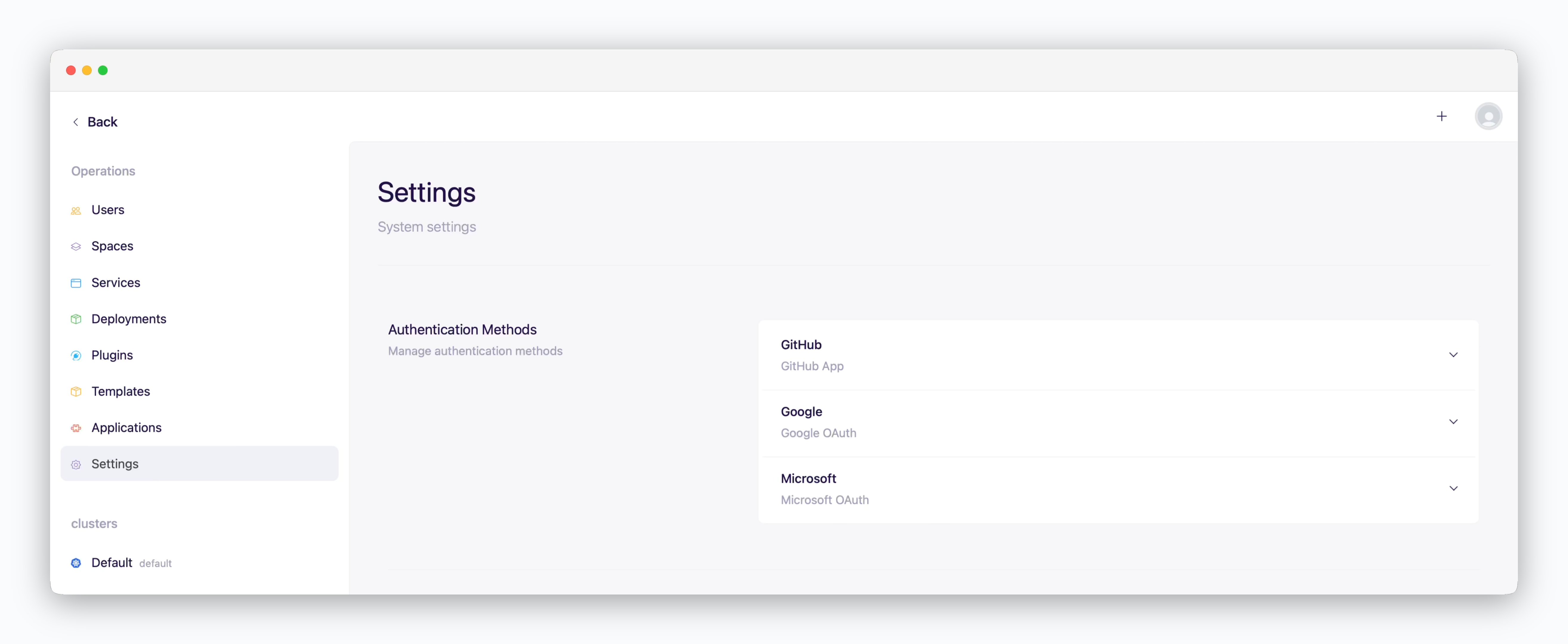
Authentication / Access Control
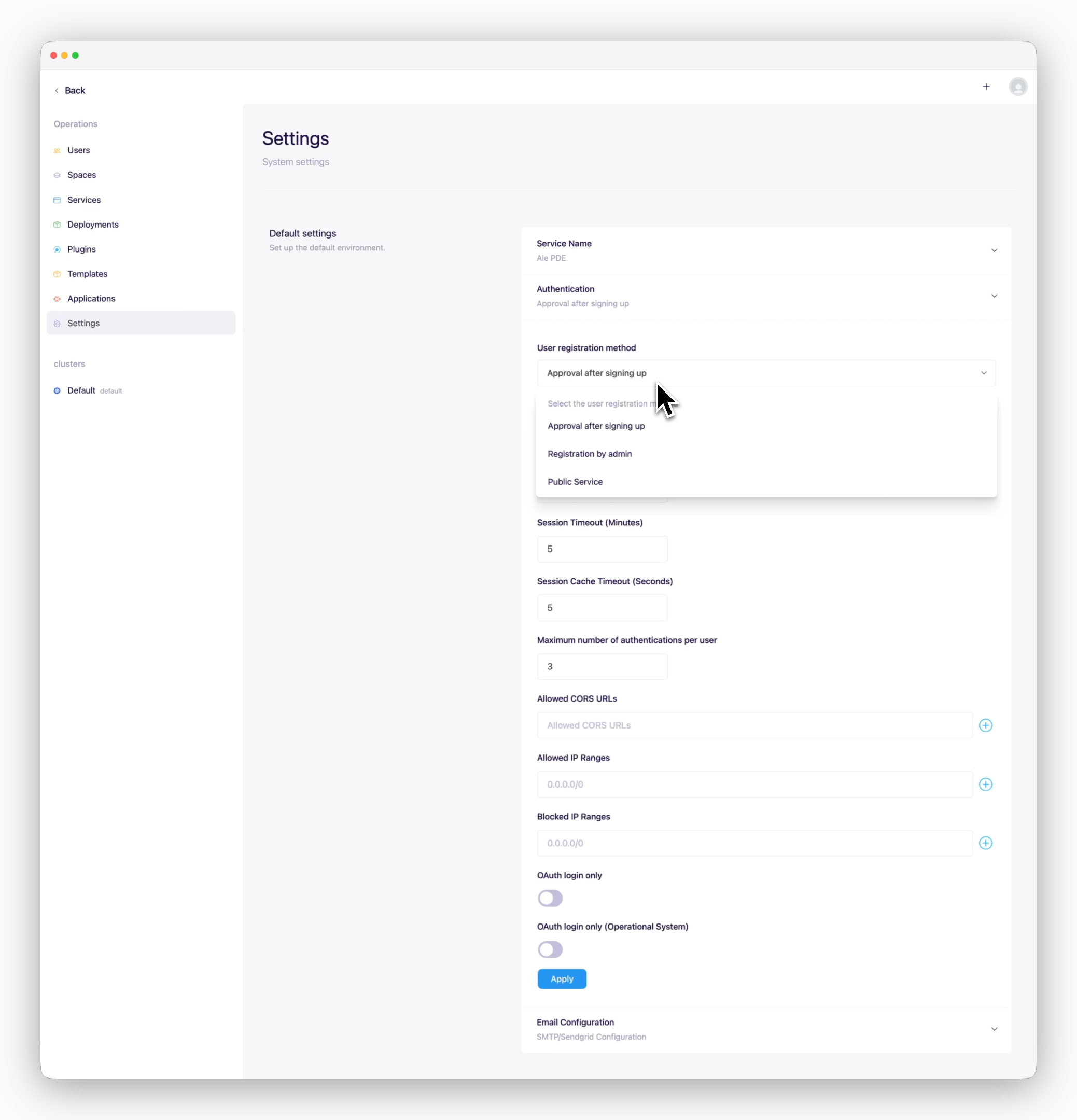
In the Authentication / Access Control section of the basic settings, you can configure various authentication and access-related settings, such as user onboarding options, session timeout duration, and allowed IP ranges for system access.
| User Onboarding Options | Sign-up and Approval Process |
|---|---|
| Approval after signing up | Users can sign up via the dashboard and need to be approved (activated) before gaining access. |
| Registration by admin | Sign-up via the dashboard is disabled. Only users registered in the operations system can access the system. |
| Public service | Users who sign up via the dashboard can access the system without approval. |
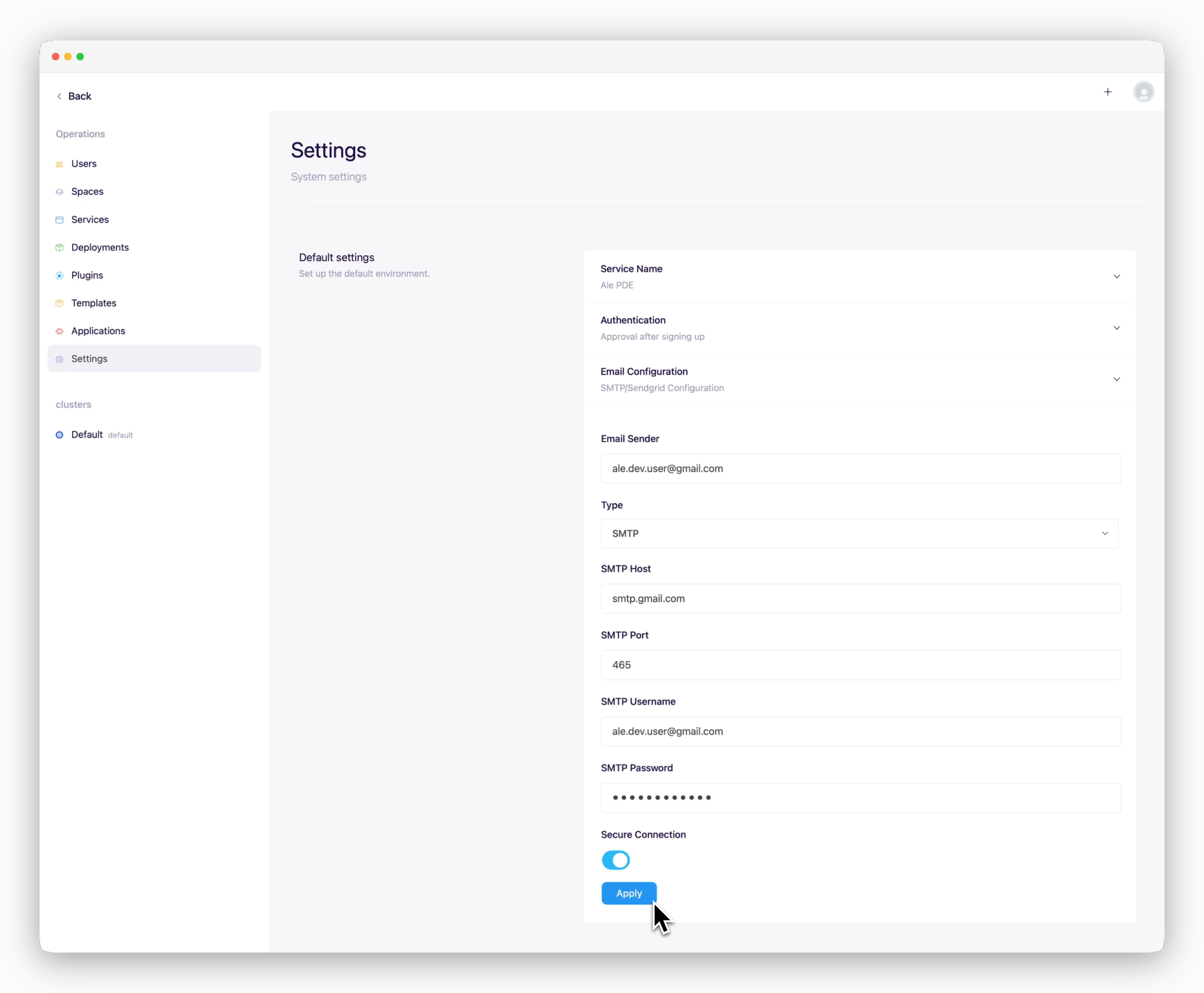
Mailer Setup
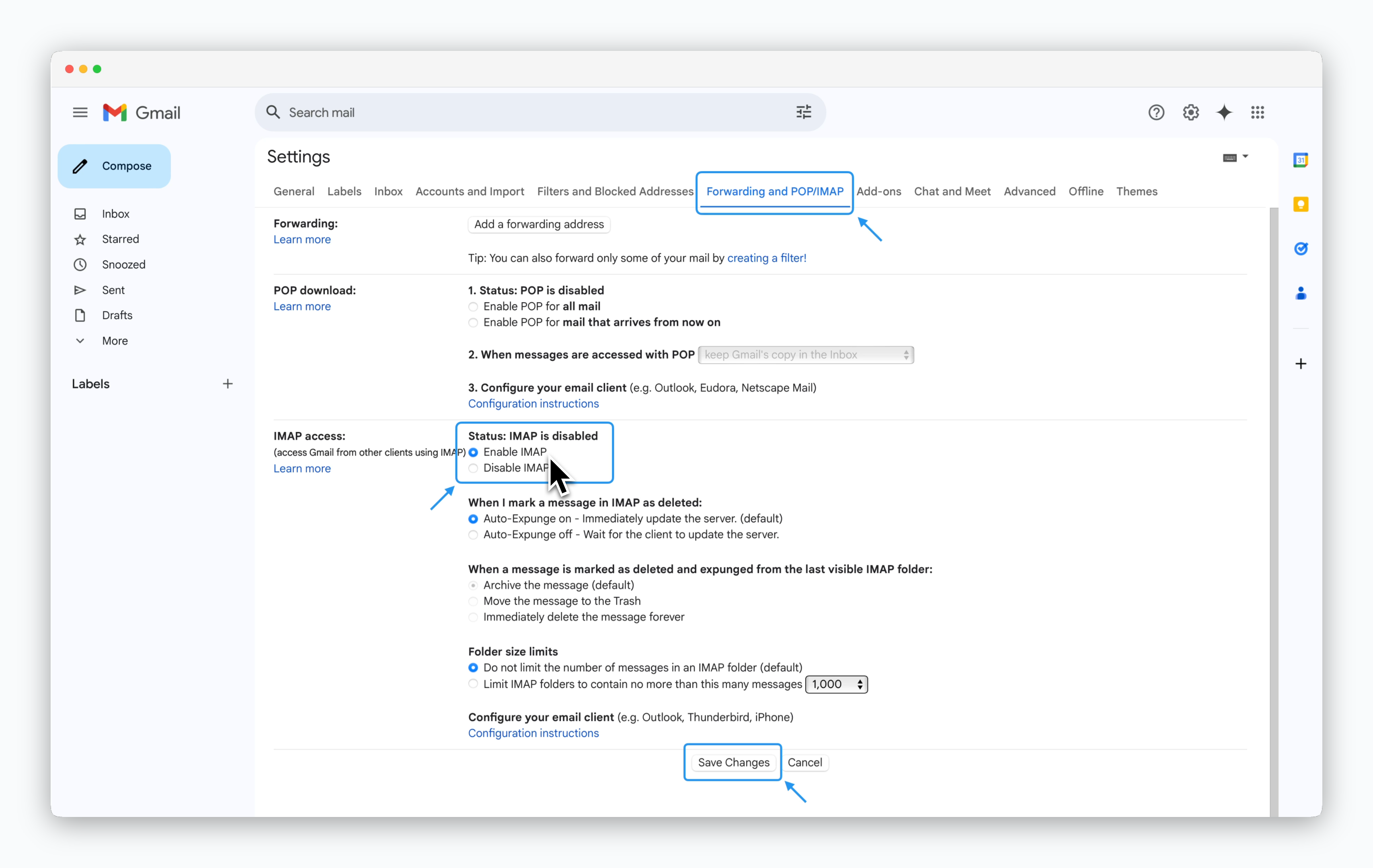
You can choose between SMTP and Sendgrid as the mailer type. If you want to use a Gmail account as the SMTP server, follow the steps below.
To use a Gmail account as an SMTP server, ensure the following settings are applied:
- Enable 2-Step Verification
- If the administrator of an organizational account has disabled the App Passwords feature due to security policies, request the administrator to enable it
Log in to the Gmail account you want to use as SMTP, click the settings icon at the top, and select 'See all settings'.
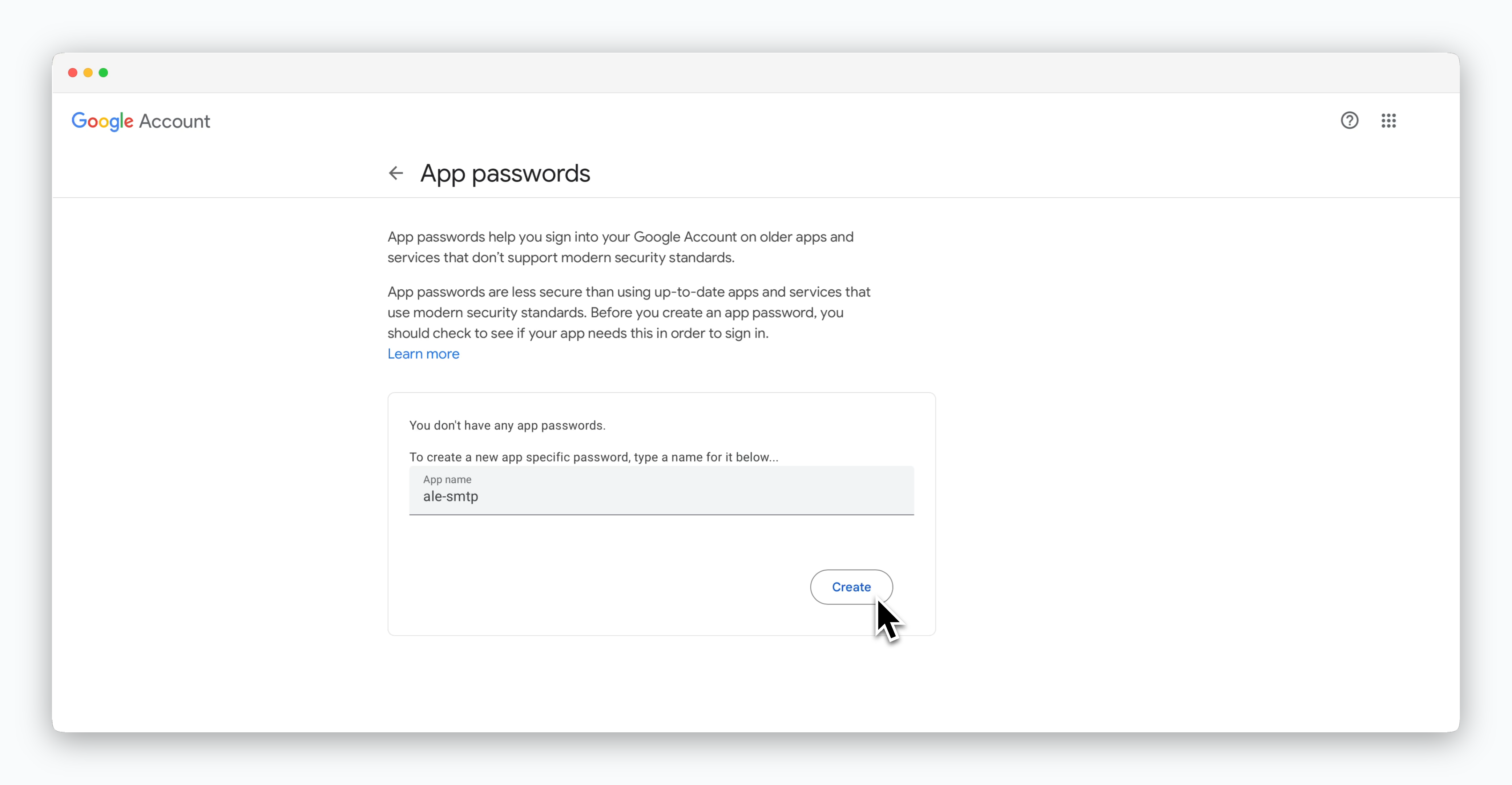
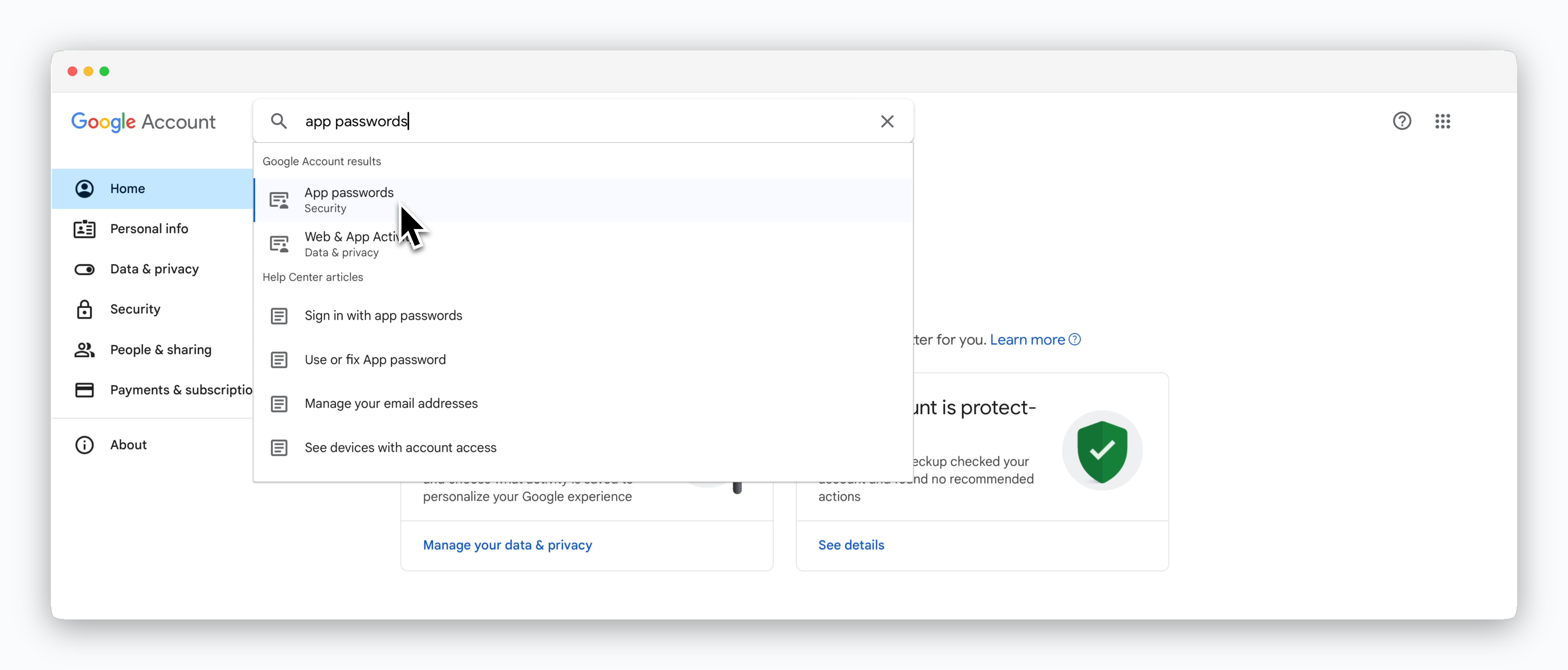
Navigate to the Google Account Management page, search for 'App passwords' in the search bar, and select it.
OAuth Setup
Resource Profile Management
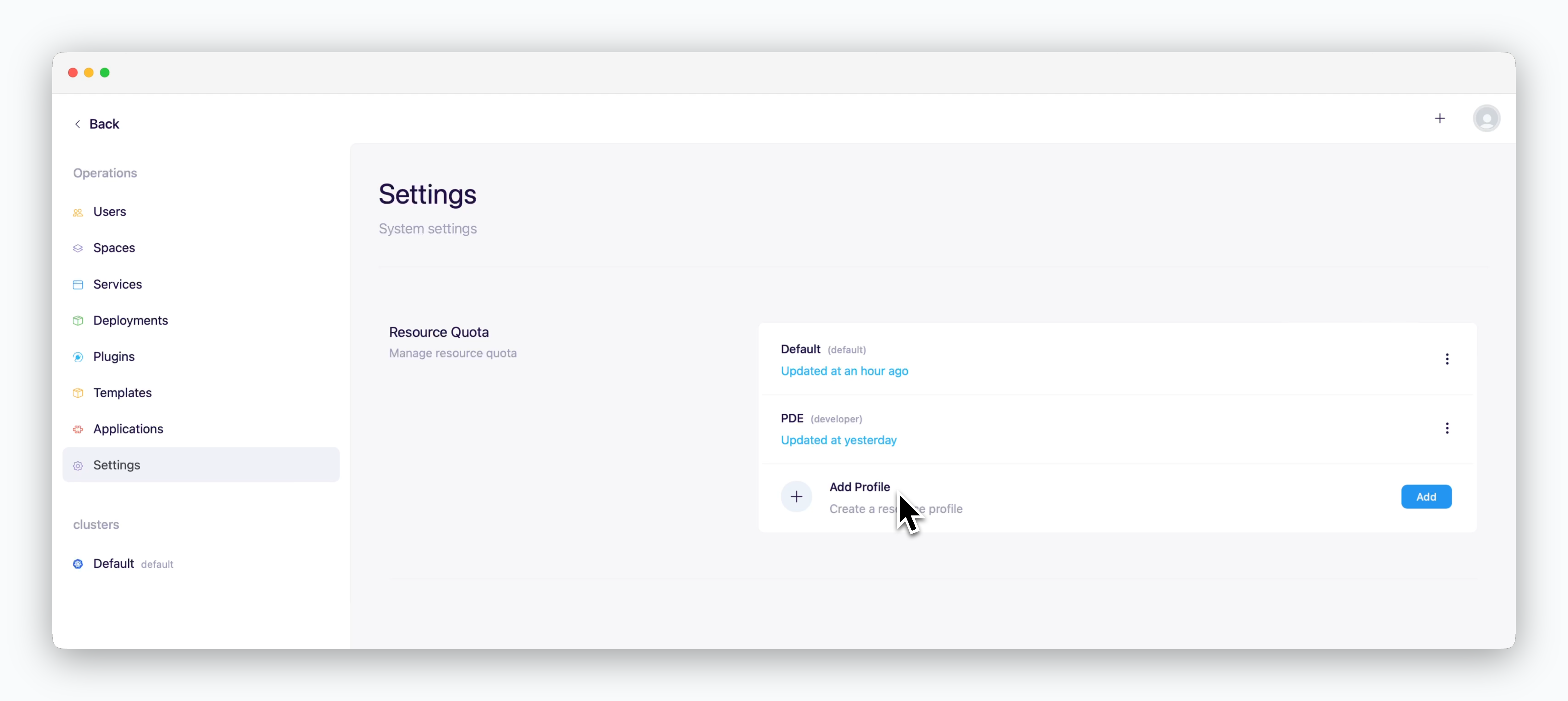
You can allocate predefined resource sets to spaces. Configure resource profiles as described below and easily assign resources by applying resource profiles to spaces.
Set Profile Name and Display Name
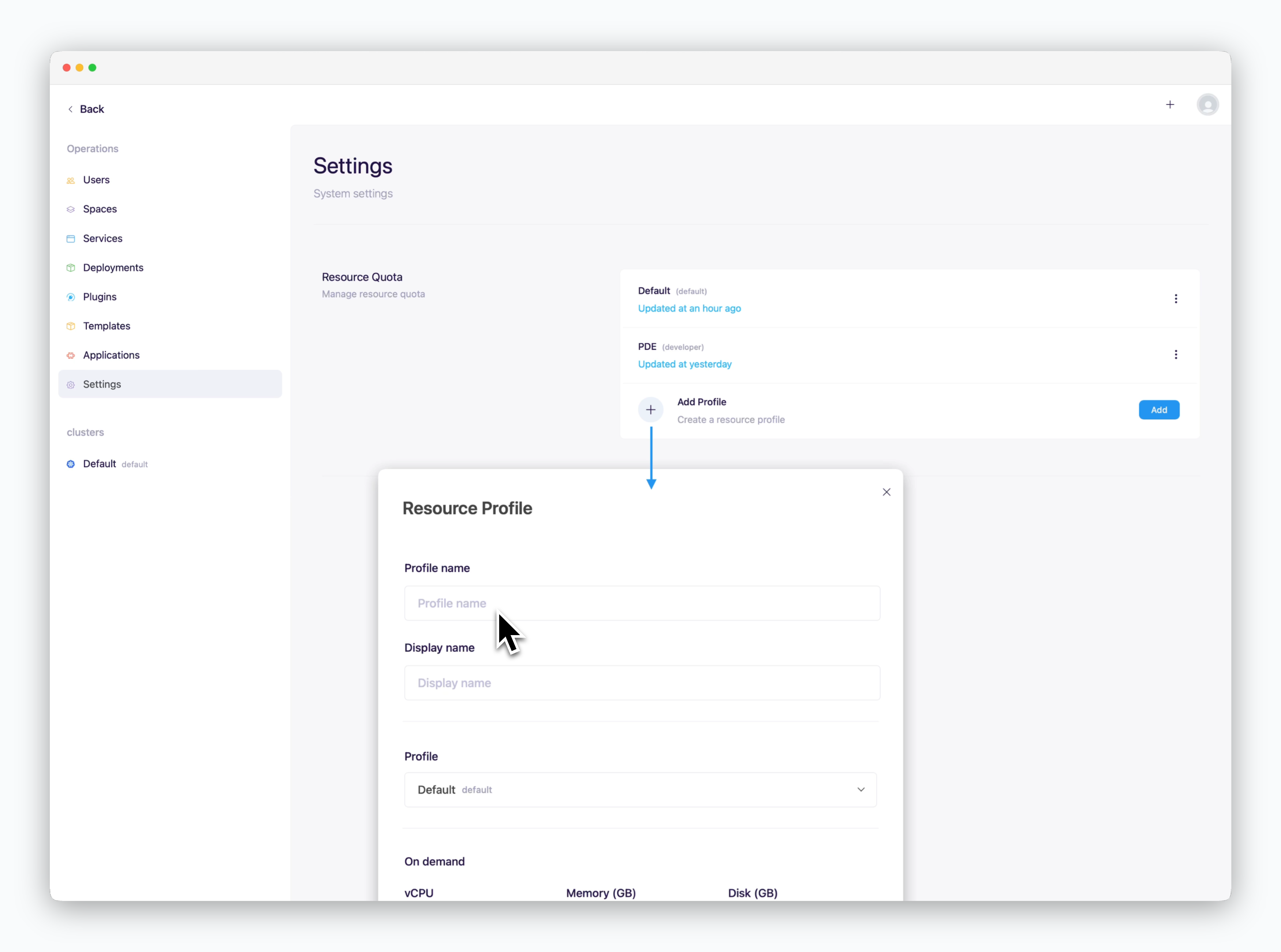
Add in the Resource Quota section and enter the profile name and the display name.Configure Resource Values for On-Demand / Spot Types
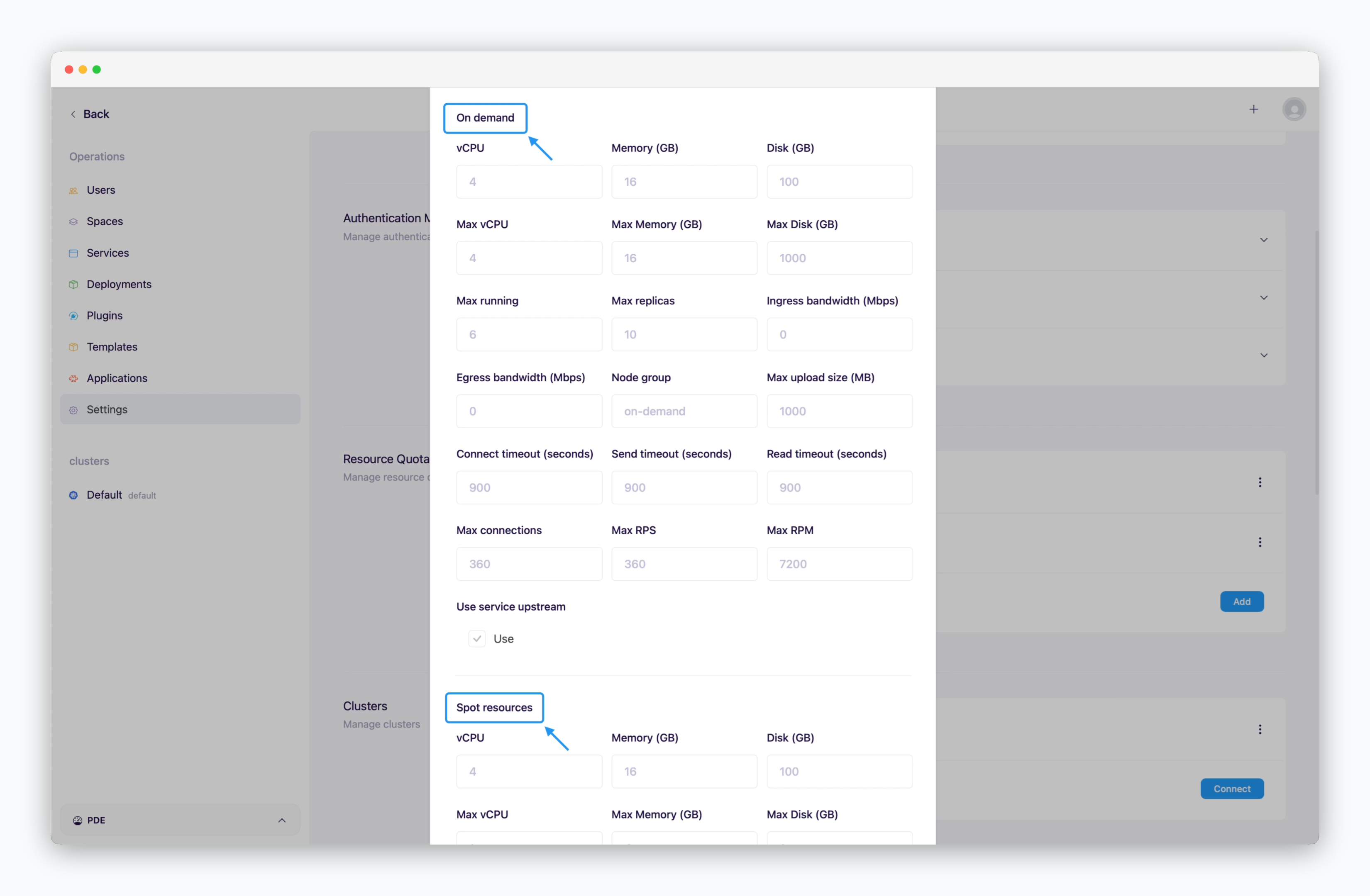
- vCPU / Memory / Disk: Total resources allocated to the space
- Max vCPU / Memory / Disk: Maximum resources per service
- Max Running: Maximum number of services that can be deployed
- Max Replica: Maximum number of replicas per service
- Node Group: Specify
on-demandorspot. See details below.
On-Demand / Spot
On-Demand / Spot
alesupports resource allocation based on instance types for efficient resource management. Specifyon-demandorspotin the Node Group field to allocate resources accordingly.
Services deployed with spot resources can be removed at once using the Bulk Remove Spot Resources feature. For temporary services, deploying with spot resources can help manage cloud costs efficiently by using this feature.

The availability and pricing policies for on-demand and spot instances differ by CSP. Refer to the following links for more information:
General Settings (Domain Connections, Team Size, etc.)
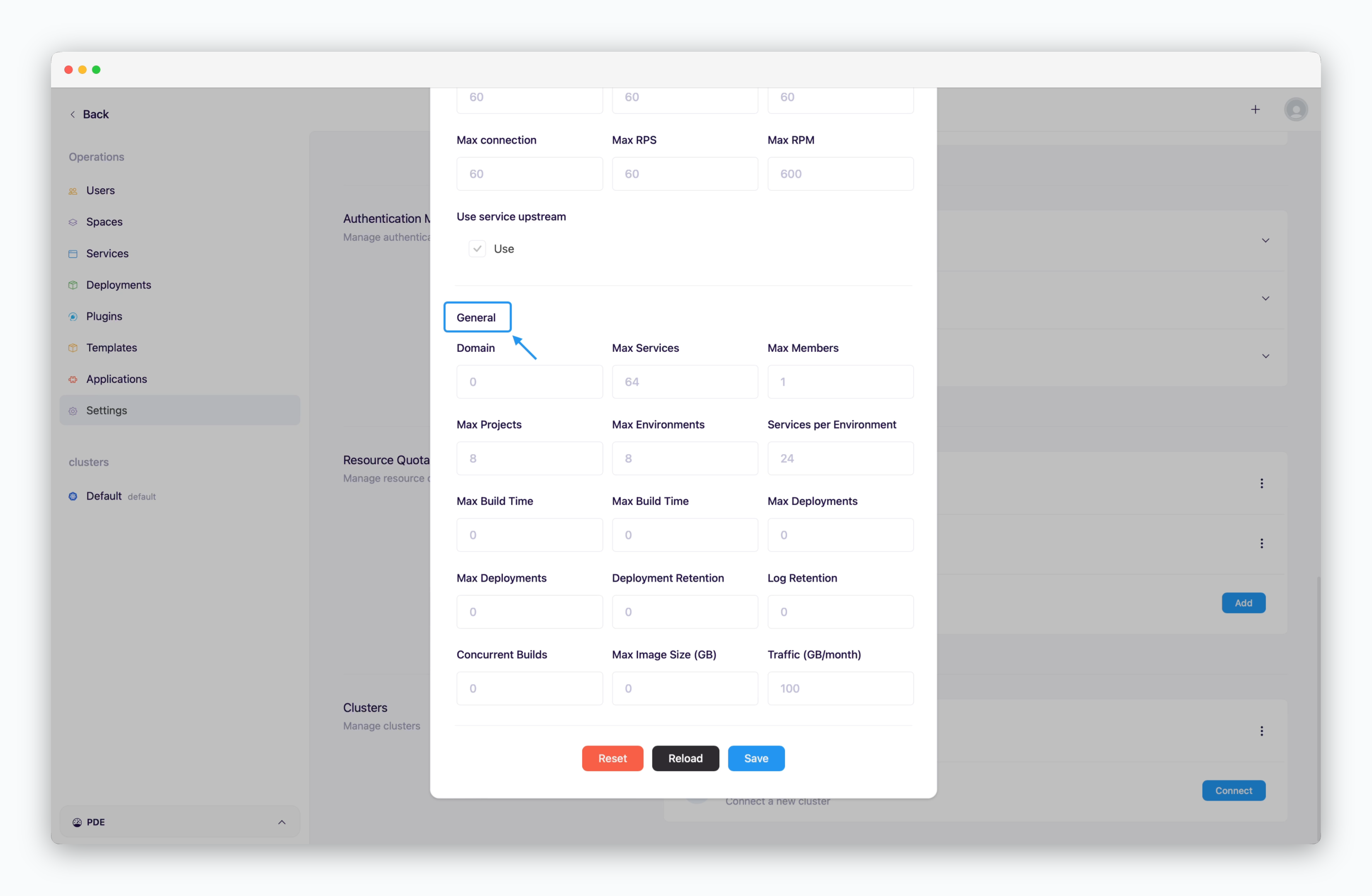
- Domain: Number of allowed custom domains (set to 0 to disable)
- Max Services: Maximum number of deployable services (including on-demand and spot)
- Max Members: Maximum number of team members allowed in the space
- Max Projects: Maximum number of projects in the space
- Services per Environment: Maximum services per environment(namespace)
- Others: If the placeholder value is 0, it will be applied as unlimited.
Add Cluster
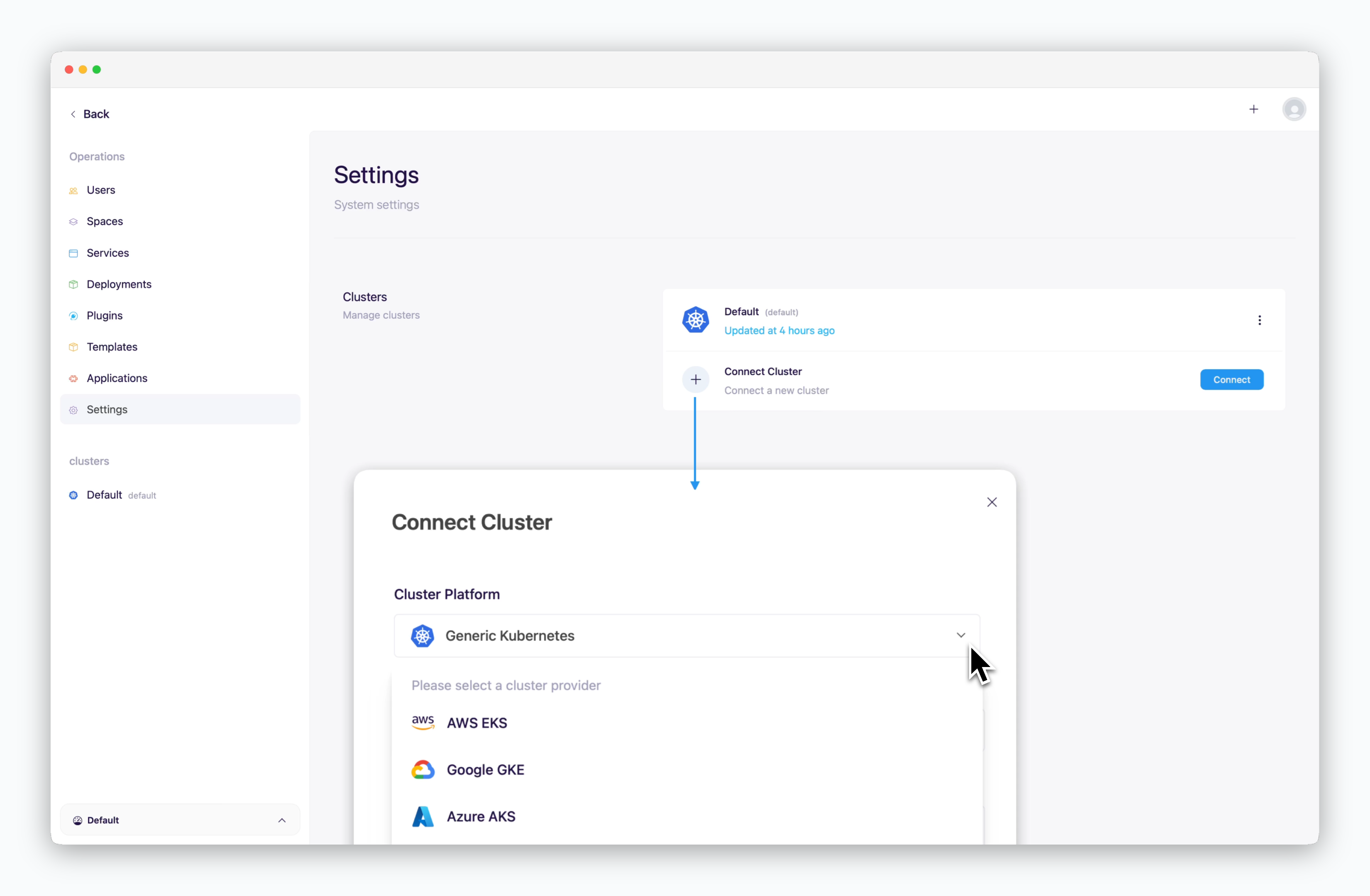
ale supports connecting to Kubernetes clusters from major CSPs as well as generic clusters. For more details on adding clusters, refer to the Multi-Cluster page.