ale provides the hostnames and ports for connecting services with other services. These connections can be set up for internal communication within the same environment or for external access.
Service Endpoints
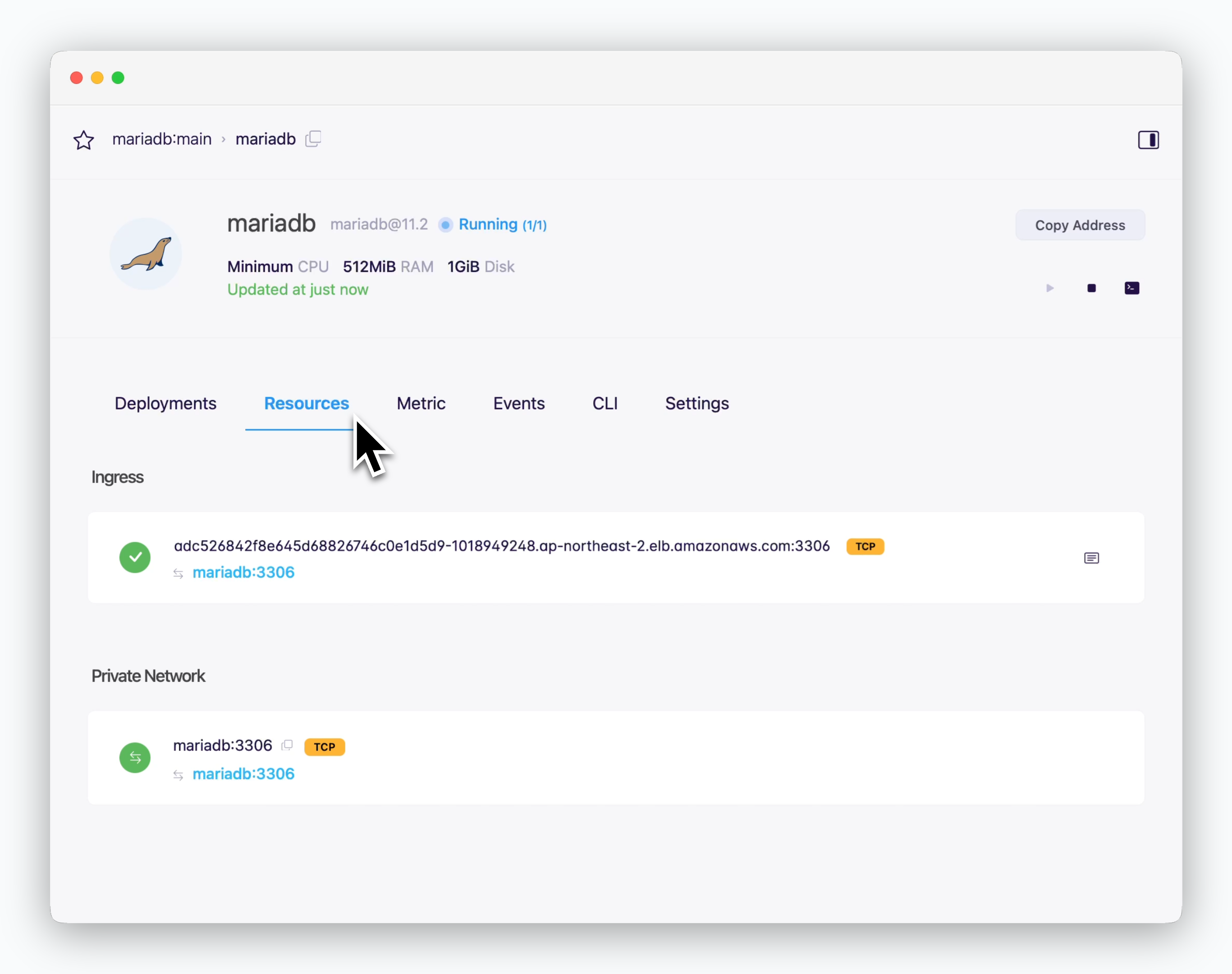
In the resource tab of the service page, you can find two types of endpoints:
- Ingress: [hostname:port] for external service connections
- Private network: [hostname:port] for connections within the same environment
Services within the same environment can connect using the service name as the hostname.
Internal Service Connection
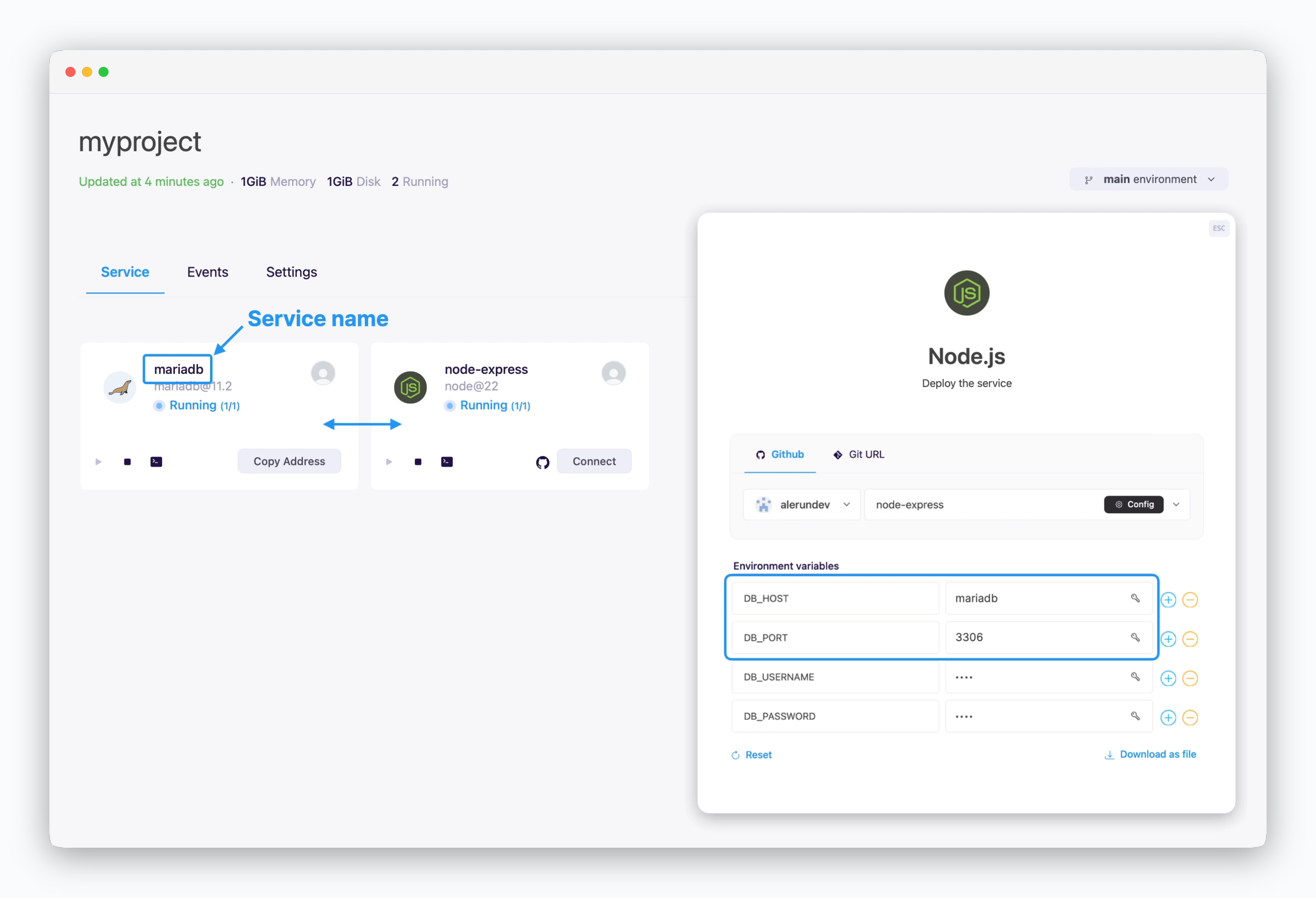
Services displayed on the same screen can communicate using the private network address, service name and port number.
Services shown together belong to the same environment (namespace). Since each environment is isolated within its own network, there’s no need for firewall rules, minimizing communication latency.
External and Cross-env Services
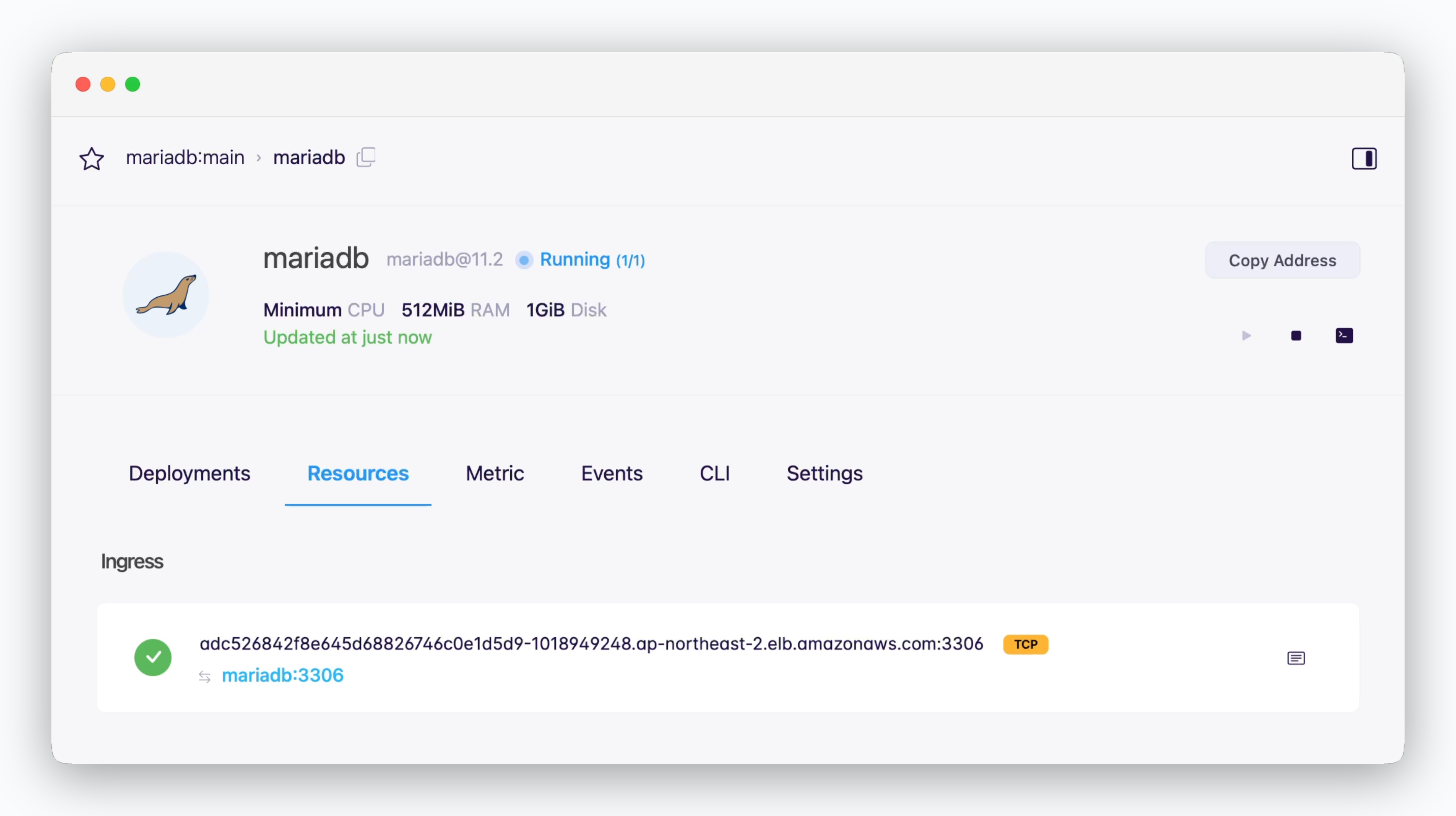
Services not in the same environment or external services can connect using ingress address shown at the top of the resource tab in the service page. For this type of connection, you should allow TCP external access in the settings tab of the environment where the database is located.
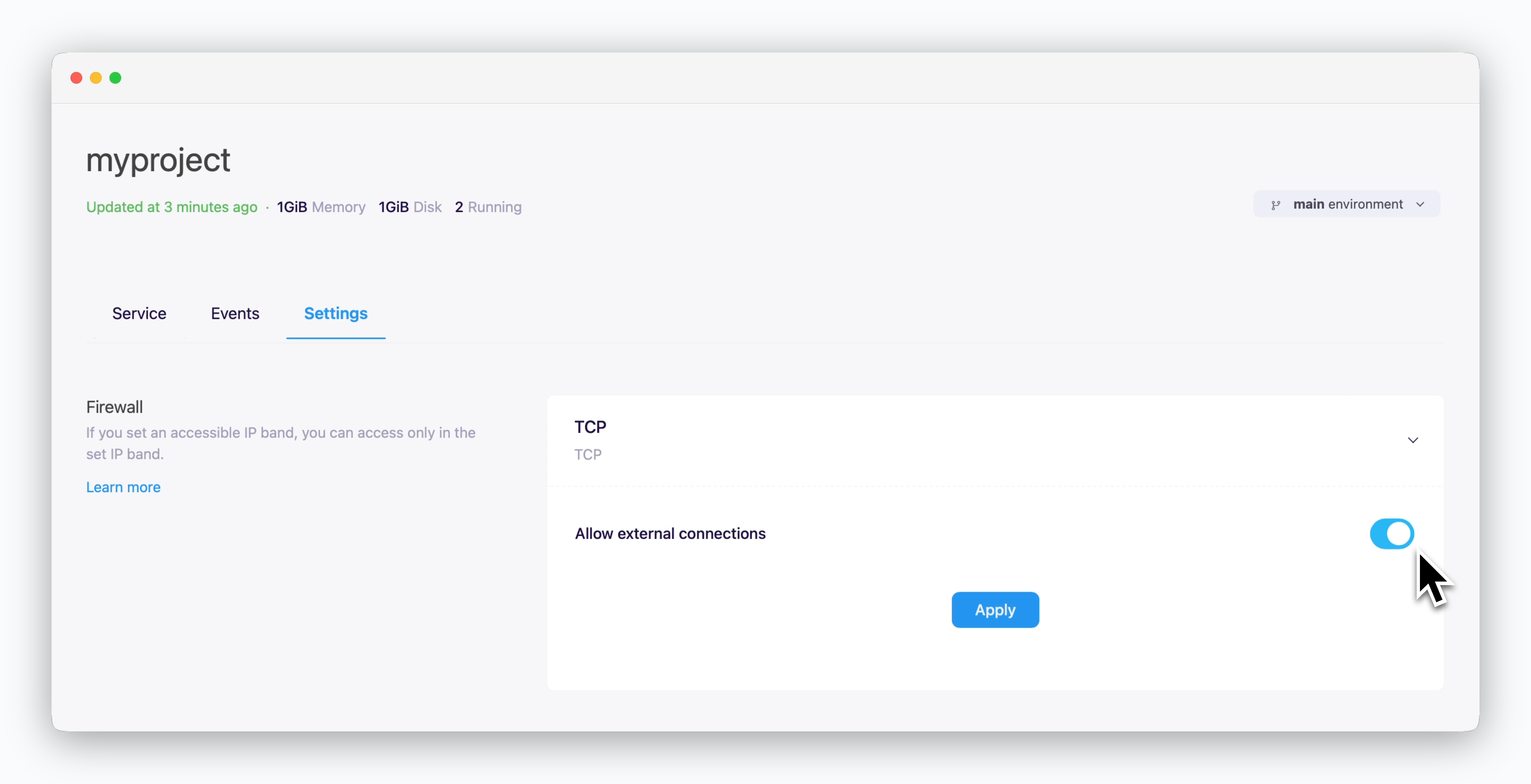
You can connect to your databases from DB client tools via TCP.
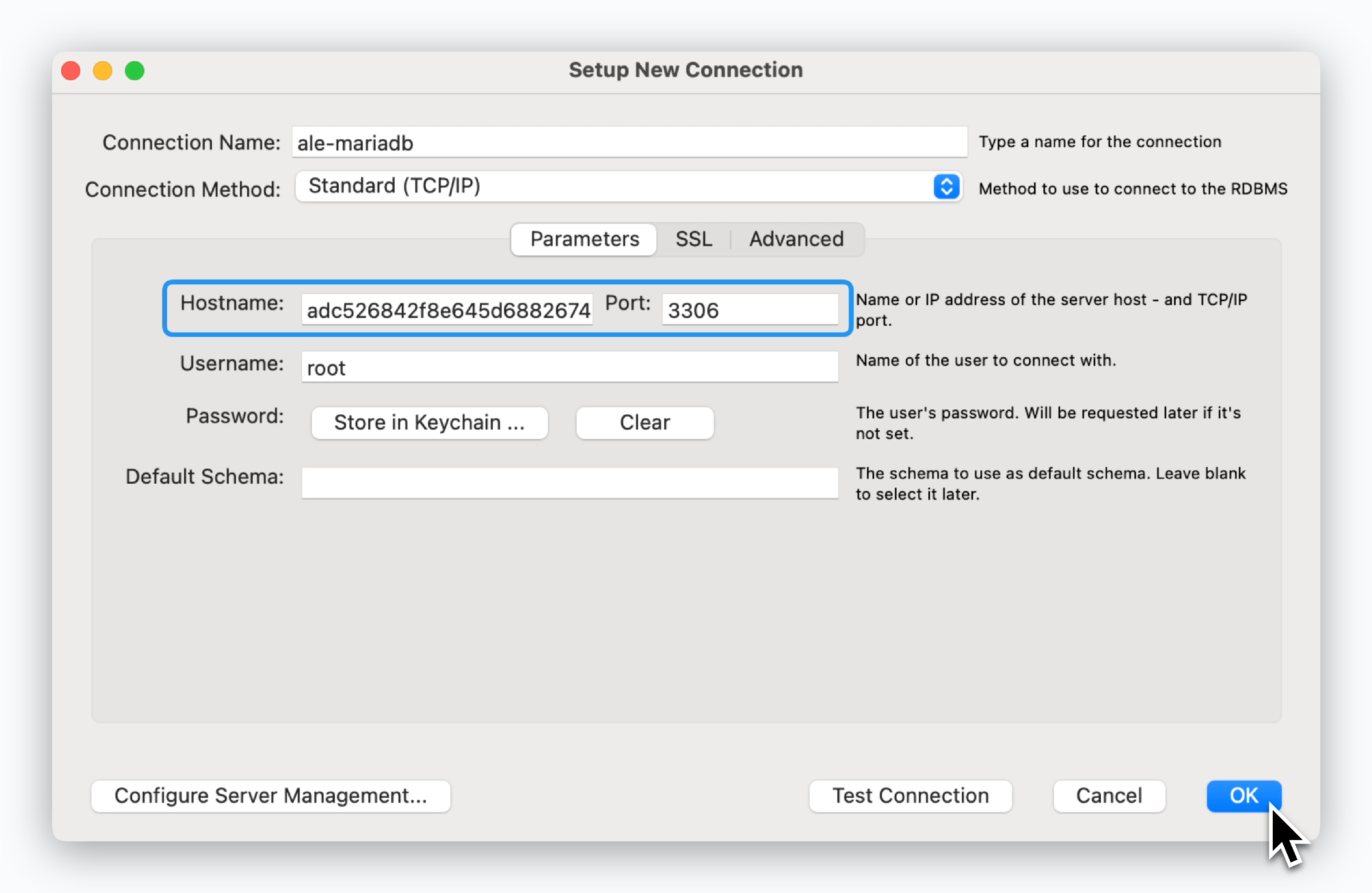
MariaDB - MySQL Workbench
MariaDB - MySQL Workbench

Enter the ingress address, then in the next screen, enter the Root Password you set during deployment.
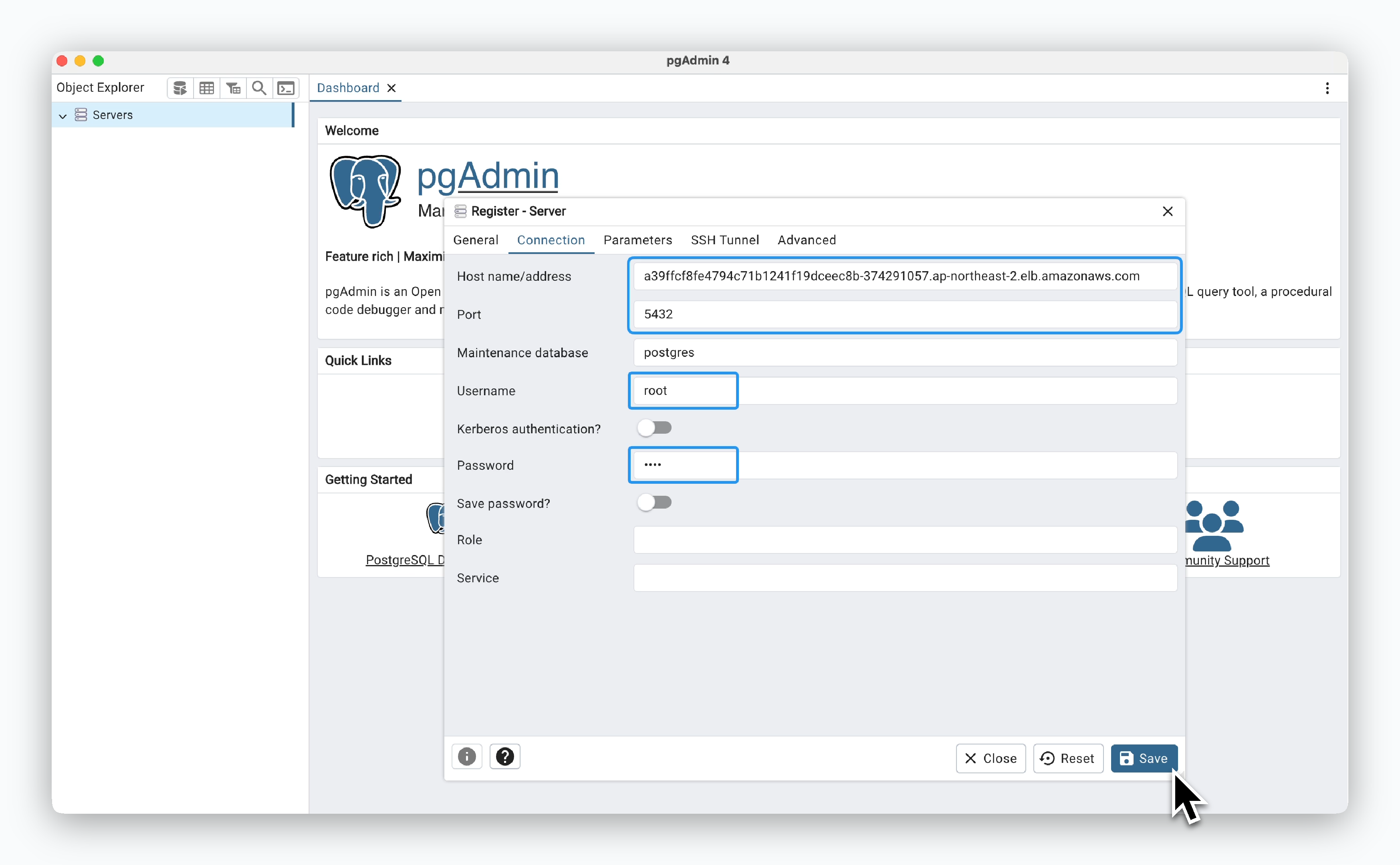
PostgreSQL - pgAdmin
PostgreSQL - pgAdmin

In the Connection tab, enter the ingress address, the Username (default is root), and the Root Password you set during deployment.
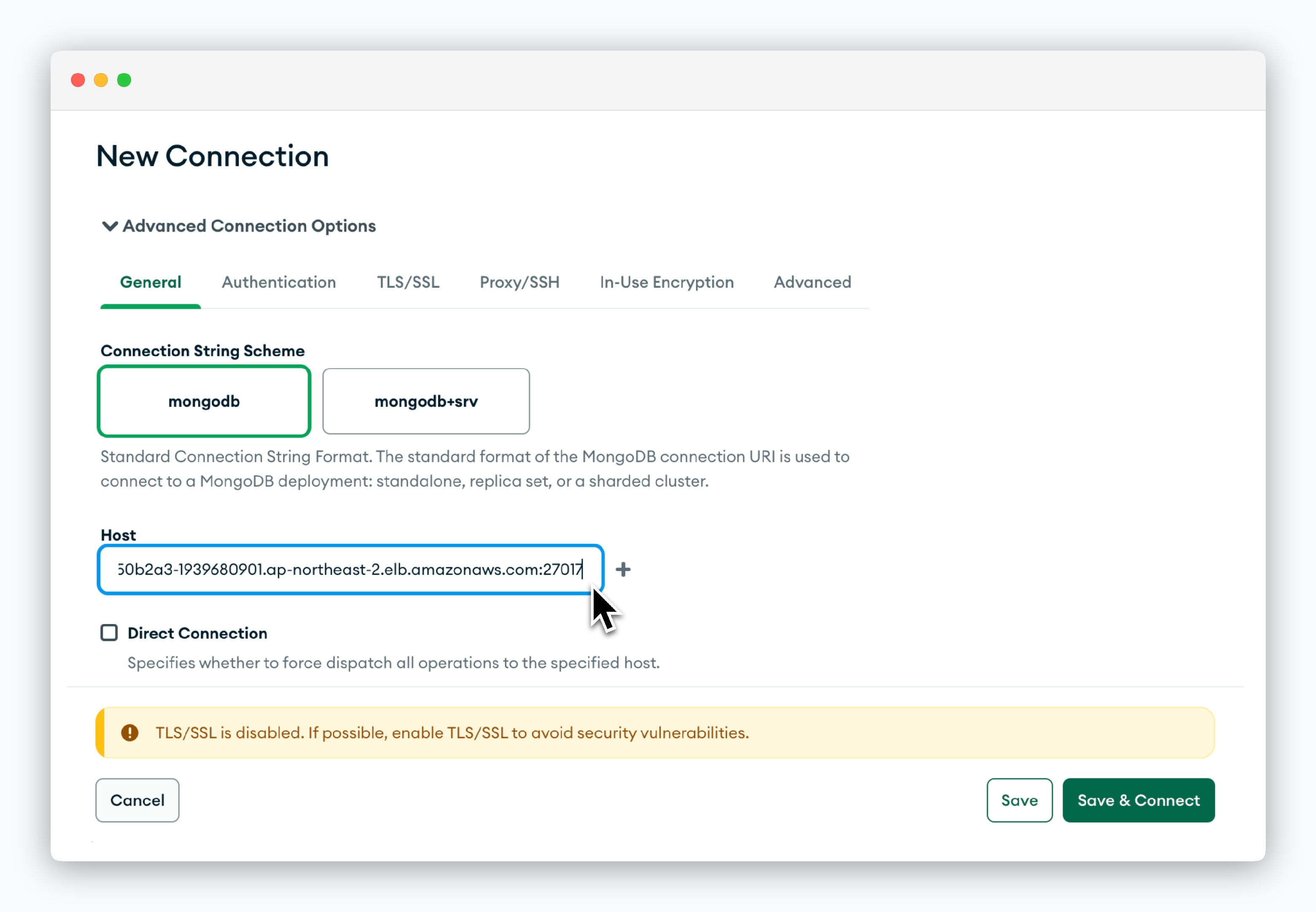
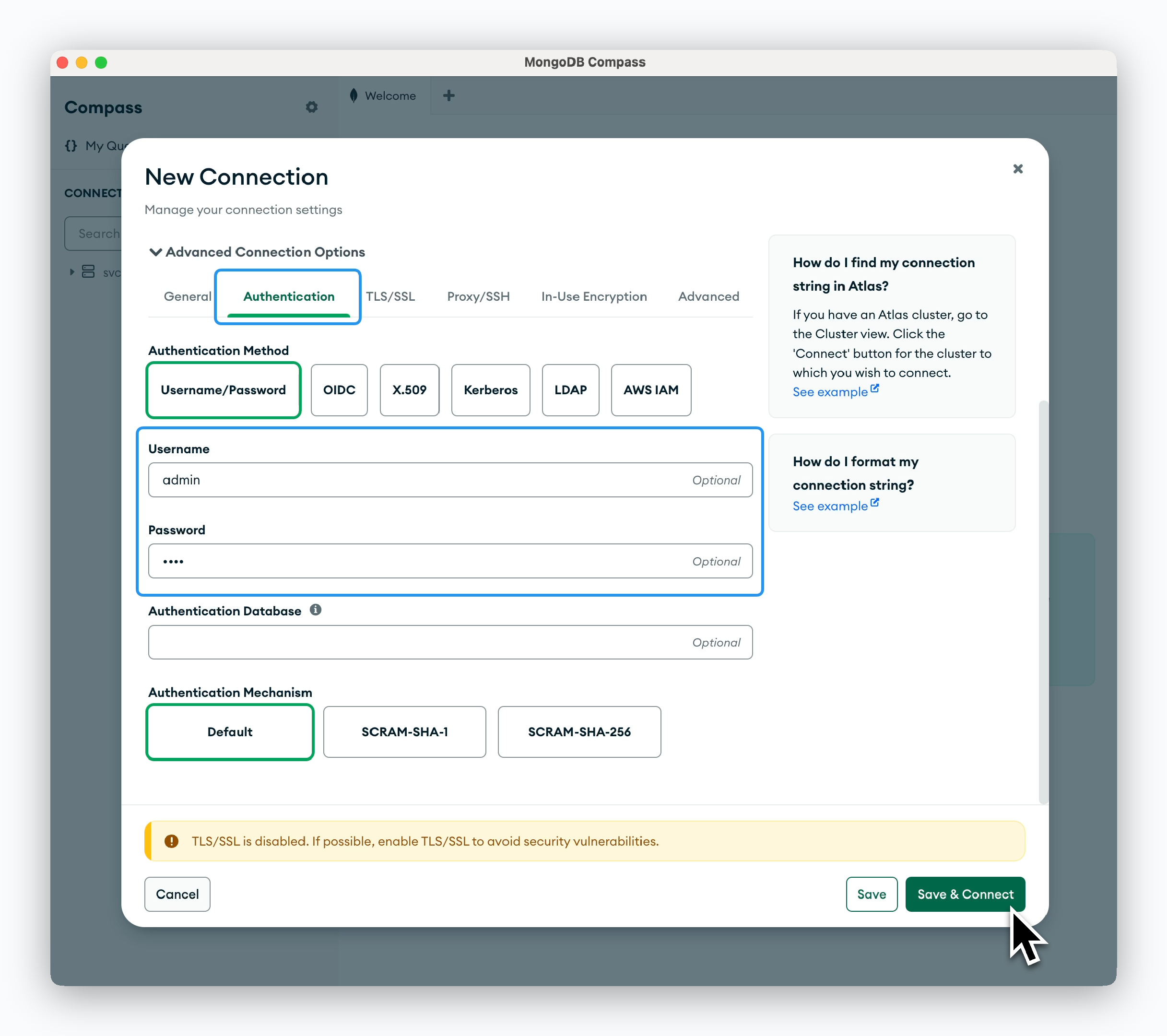
MongoDB - MongoDB Compass
MongoDB - MongoDB Compass

Click New Connection, then in the Advanced Connection Options section, enter the hostname including the port number in the Host field.

In the Authentication tab, enter the Username (default is admin) and the Root Password you set during deployment.
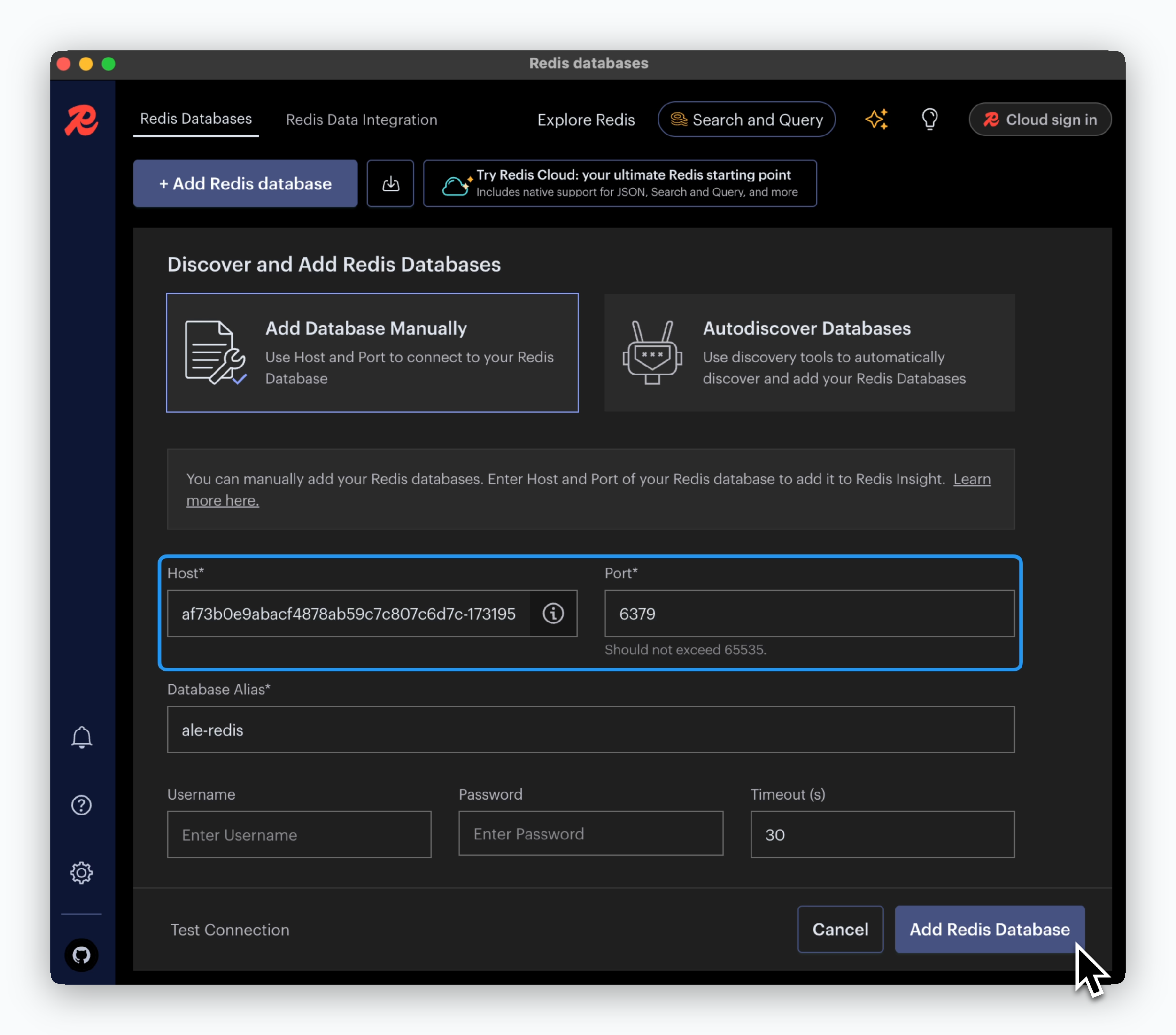
Redis - Redis Insight
Redis - Redis Insight