This guide covers database deployment in ale, service connectivity, and database management tool configuration using TCP connections.
ale offers pre-configured database options as built-in applications. For unsupported databases, you can create custom plugins through our plugin system. See our plugin guides for details.Deploying a Database
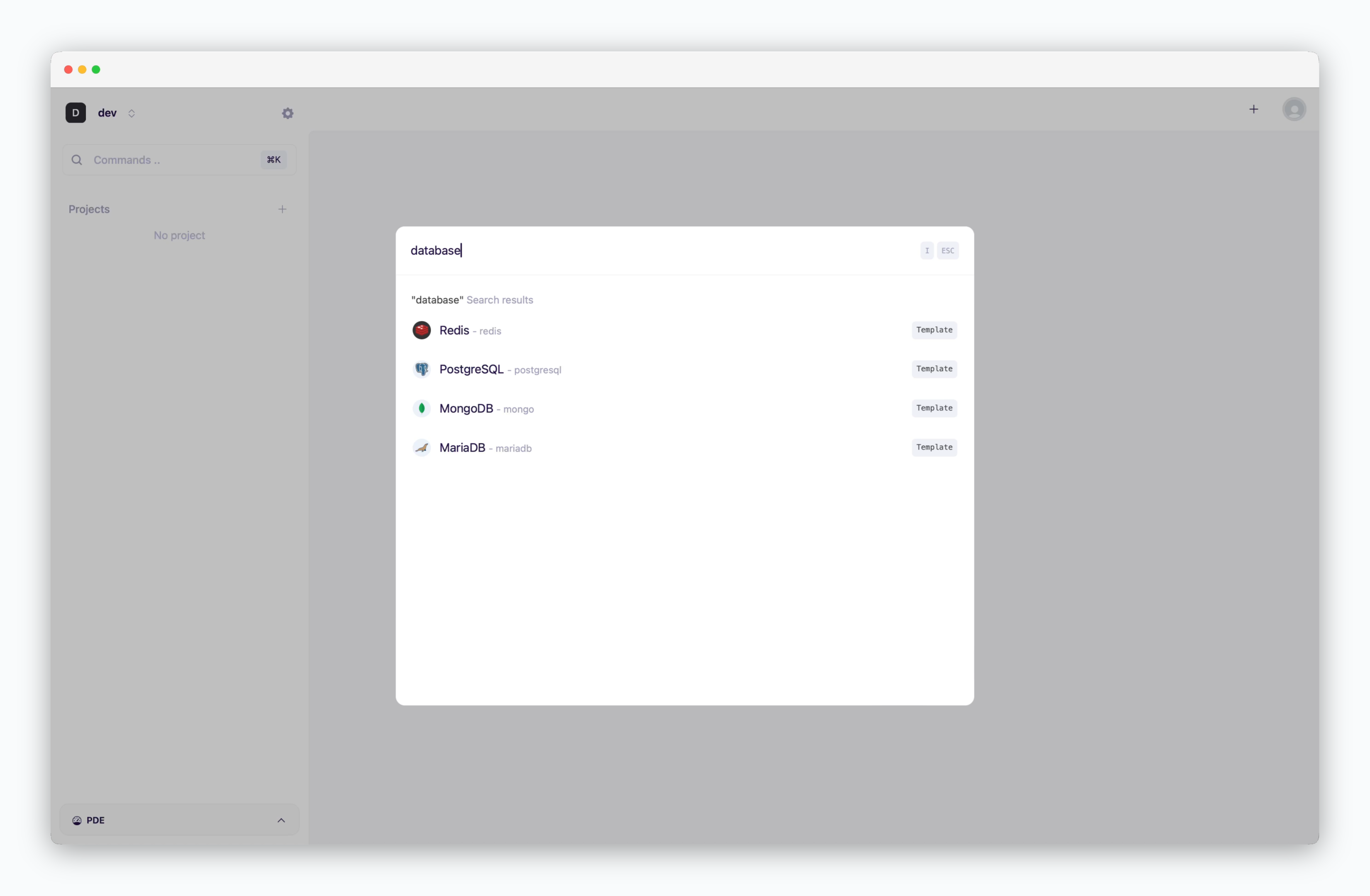
On the dashboard, click or ⌘ + K to open the deployment modal. Select the database you want to deploy and fill in the configuration fields.
Basic Configuration
Basic Configuration
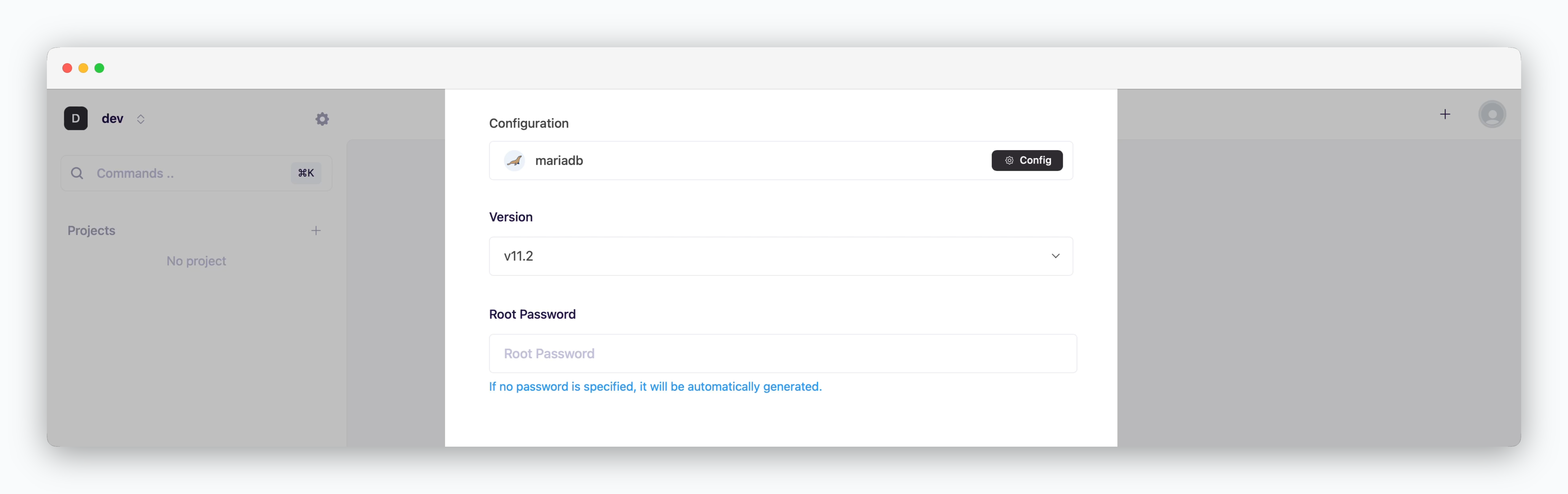
Specify the version and root password credentials.
Basic Configuration options are service-specific. Set the required values based on the deployment requirements.
More Options
More Options
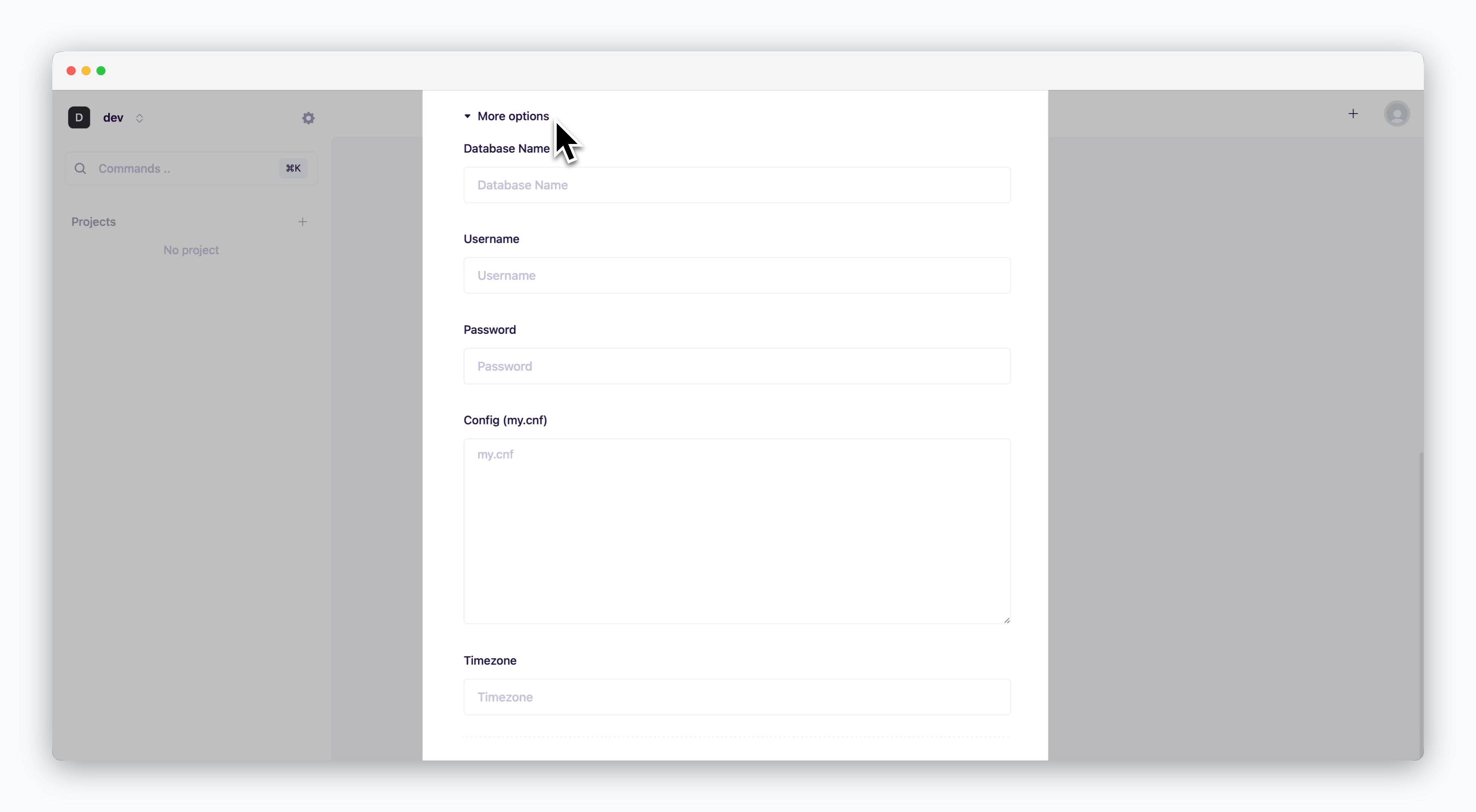
Set database name, timezone, and service-specific parameters.
Additional Options are service-specific. Configure the settings based on the selected database service and deployment requirements.
Resource Settings and Deployment
Resource Settings and Deployment
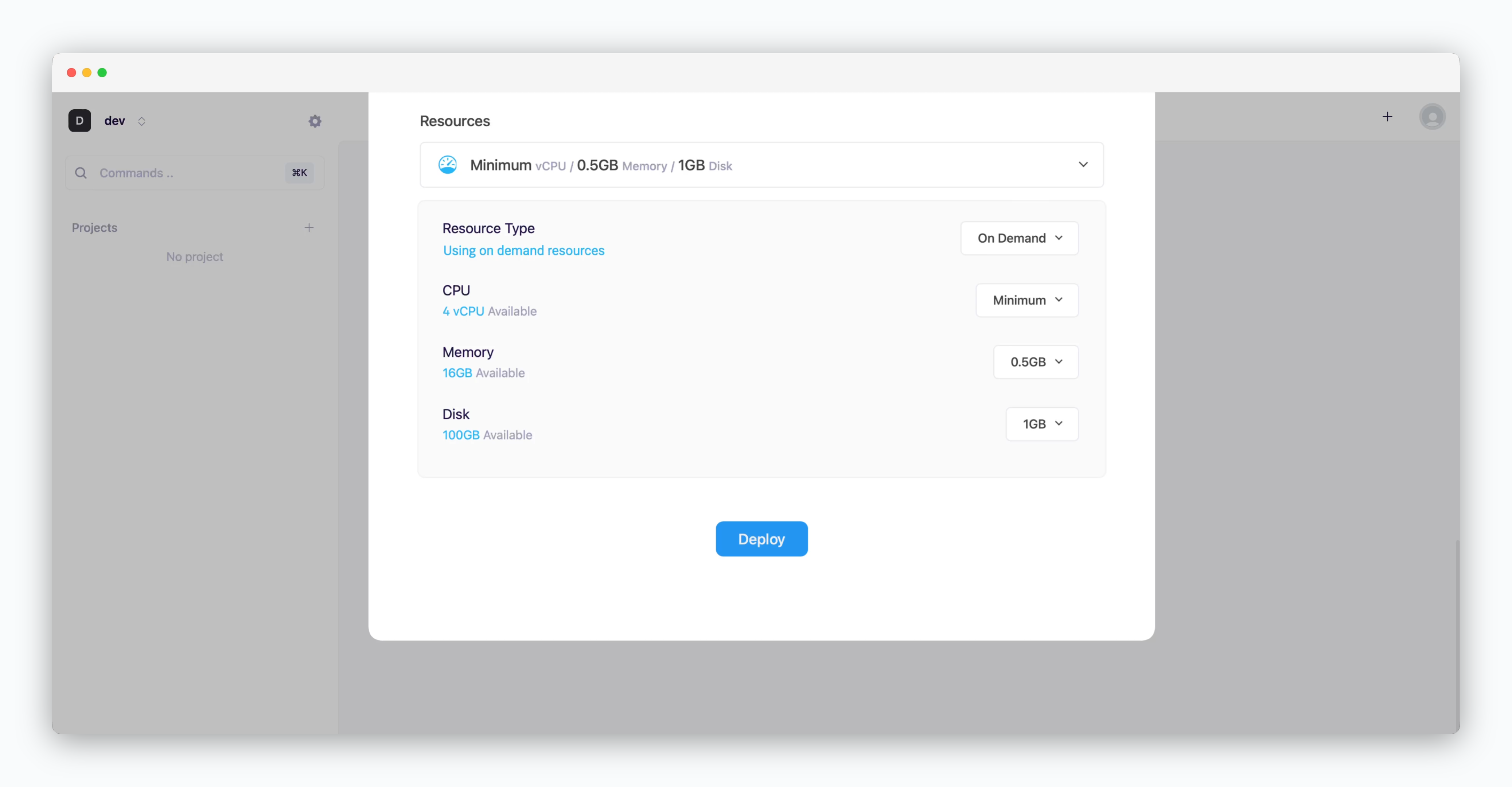
- Resource Type: Select between On-demand or Spot instance types
- CPU: Maximum vCPU resource for the service. Minimum vCPU means 0.1 vCPU
- Memory: Maximum memory size the service can use
- Disk: Database disk capacity
- Deploy: Click
Deploy
If deployment fails due to resource limitations, see the Space and Resource Management page to add resources to the space.
Database Connectivity
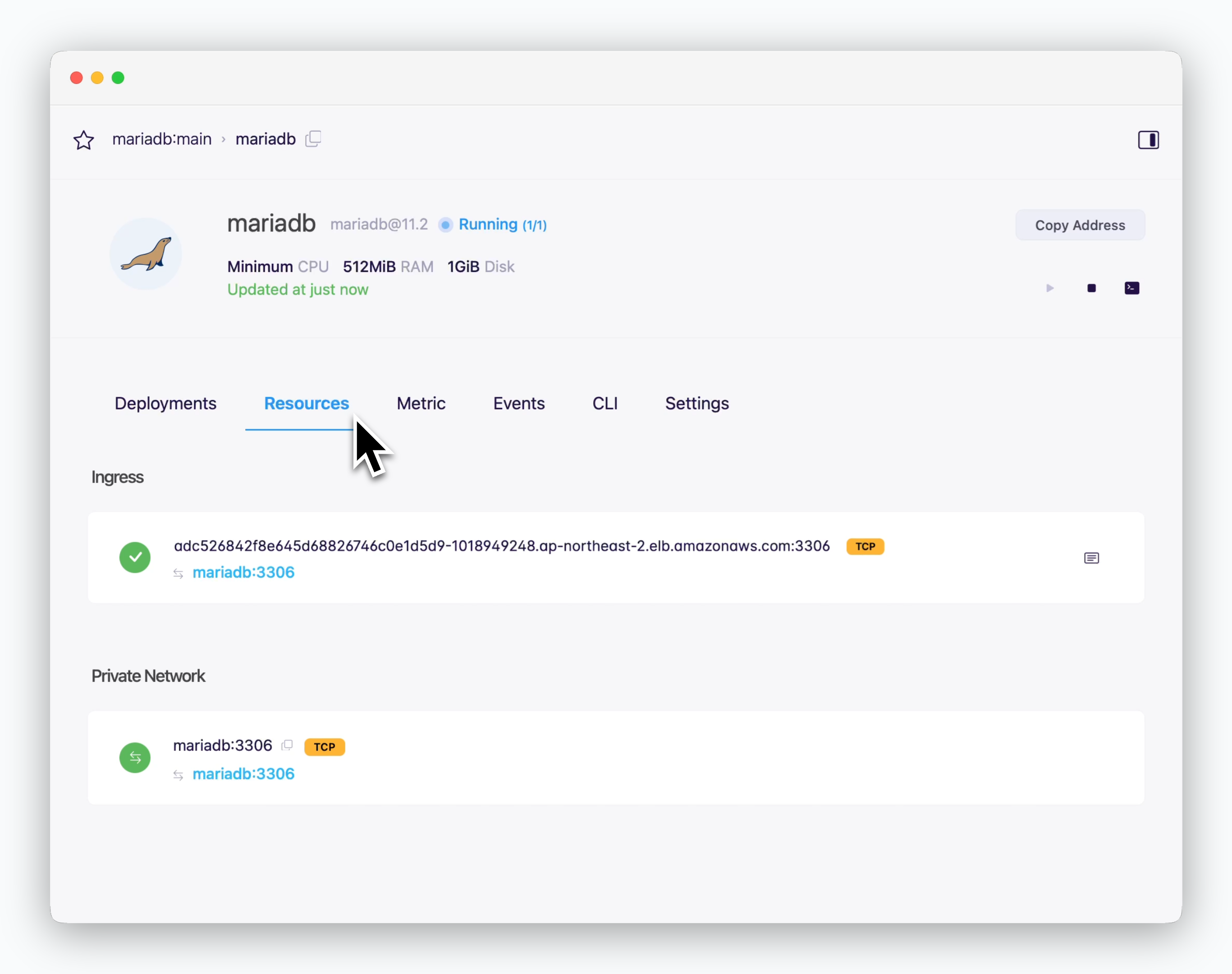
the connection info (hostname: port) is in the resources tab of the service page.
Internal Services
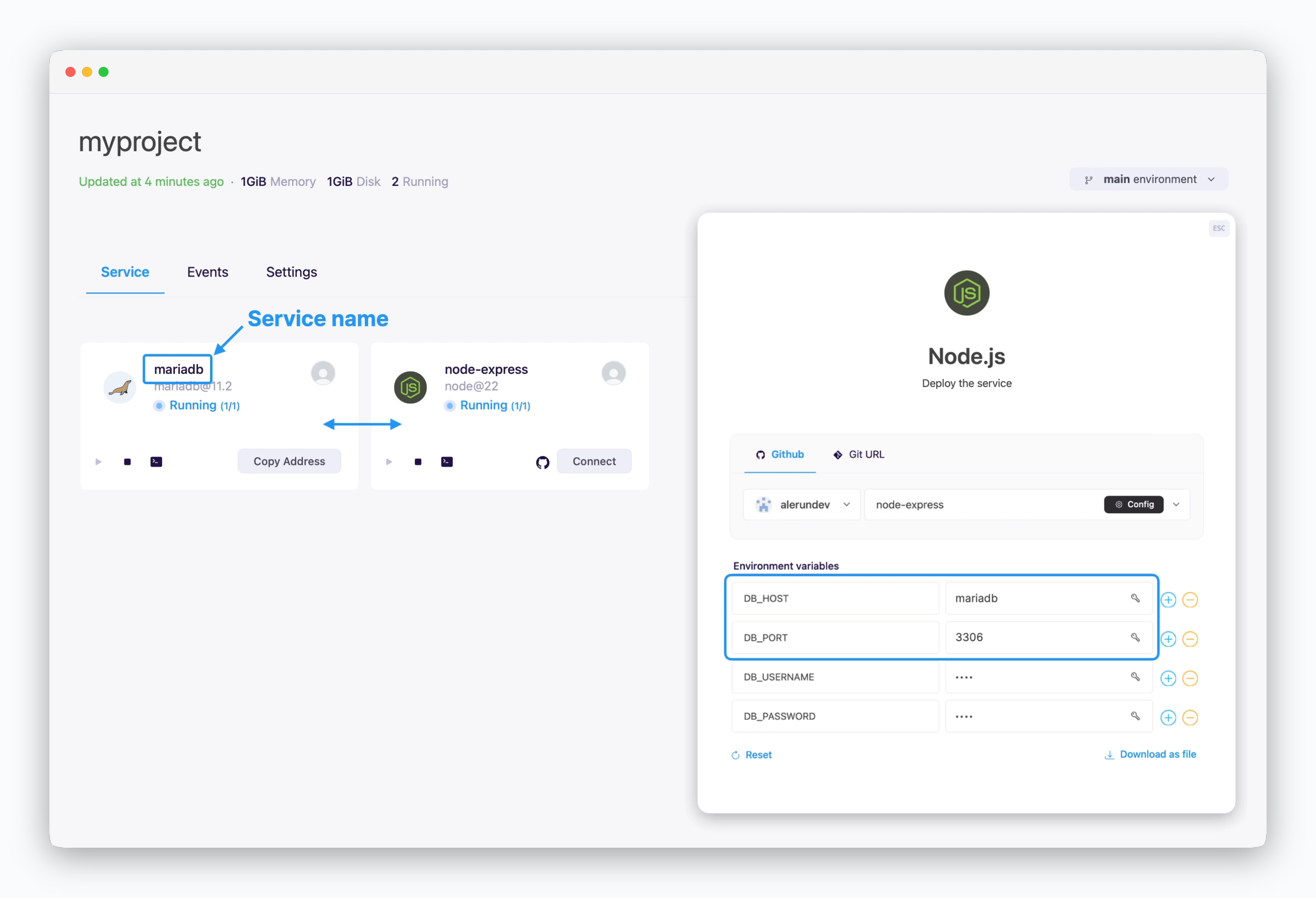
Services displayed on the same screen can communicate using the private network address, service name and port number.
Services shown together belong to the same environment (namespace). Since each environment is isolated within its own network, there’s no need for firewall rules, minimizing communication latency.
External and Cross-env Services
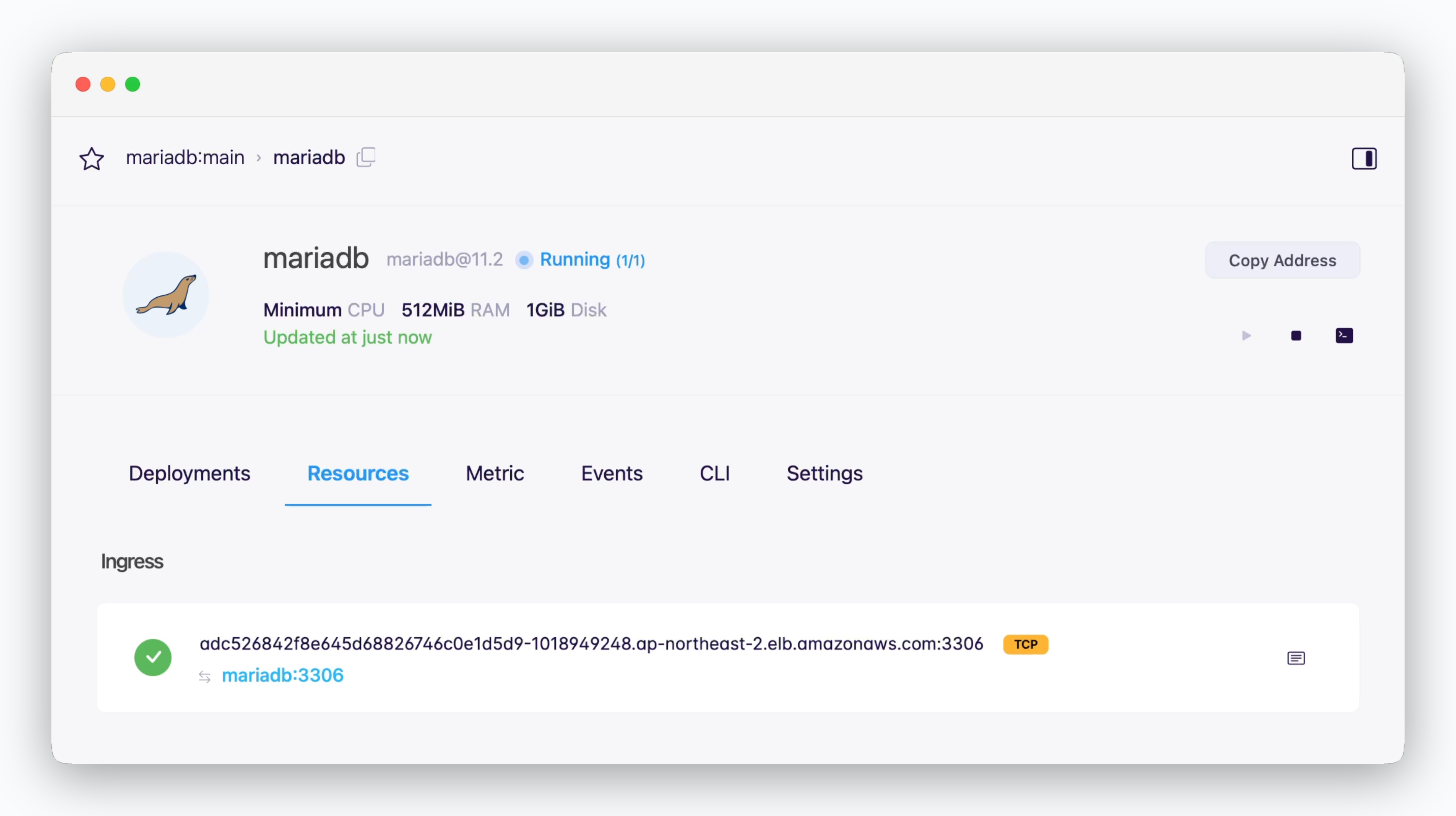
Services can connect to services in other environments or external systems using the ingress address (hostname:port). In this case, as shown below, you’ll need to allow external connections in the Settings tab of the environment where the database is deployed.
TCP External Connections
TCP External Connections
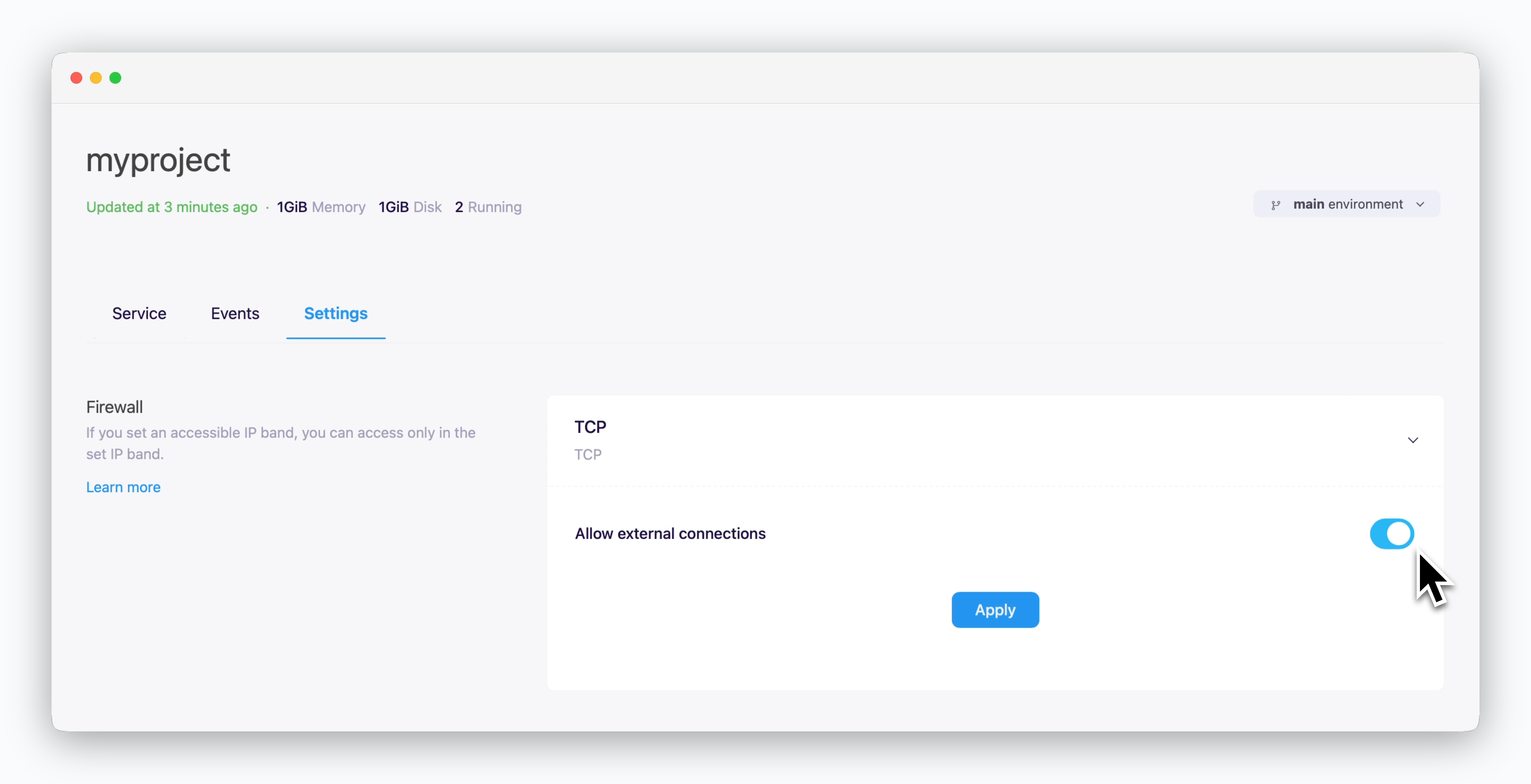
You can allow TCP external connections in the settings tab of the environment where the database you want to connect to is located.
Database Client Tools
You can use the ingress address to connect to your database from DB client tools via TCP.
MariaDB - MySQL Workbench
MariaDB - MySQL Workbench
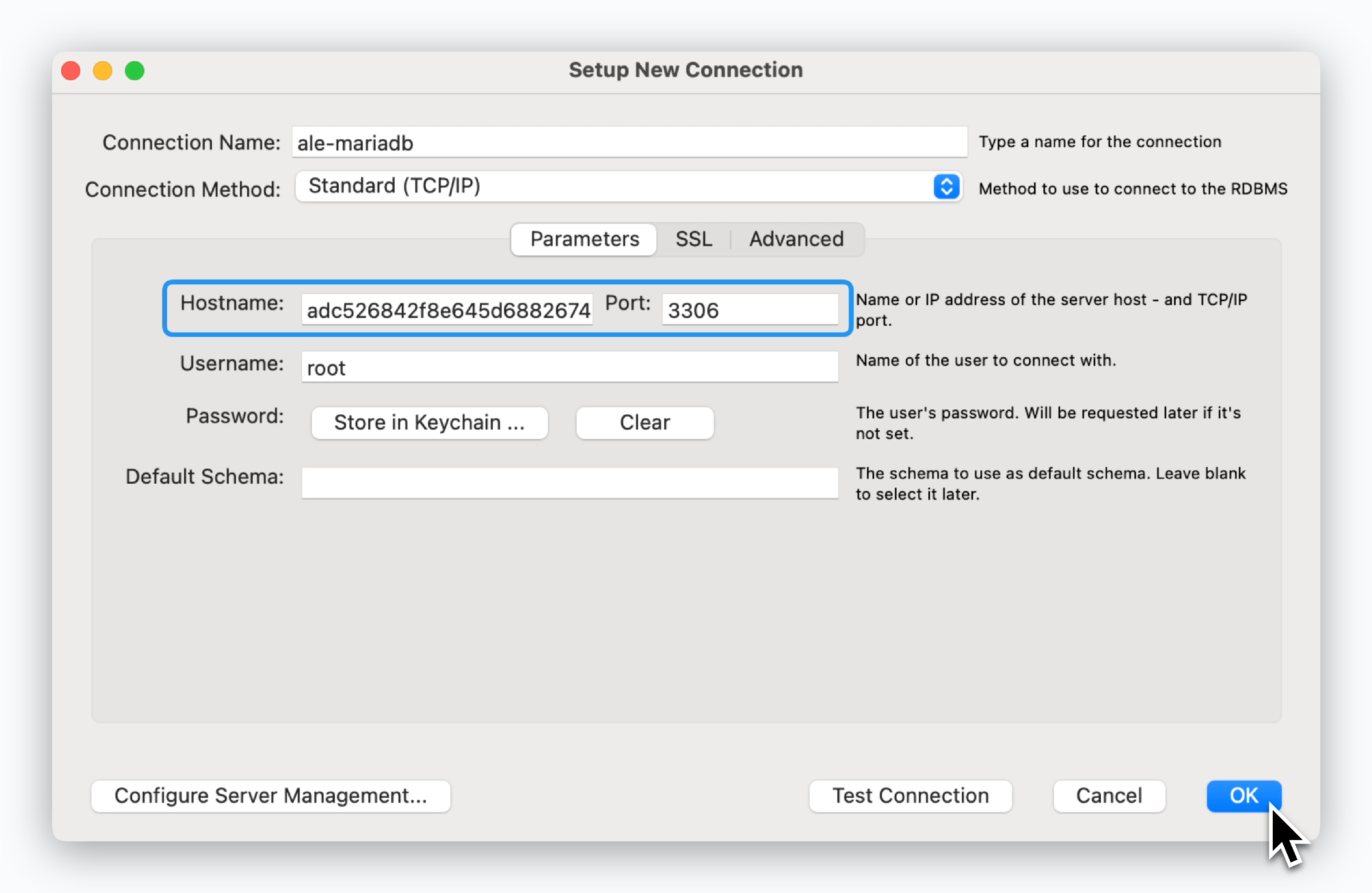
Enter the ingress address, then in the next screen, enter the Root Password you set during deployment.
PostgreSQL - pgAdmin
PostgreSQL - pgAdmin
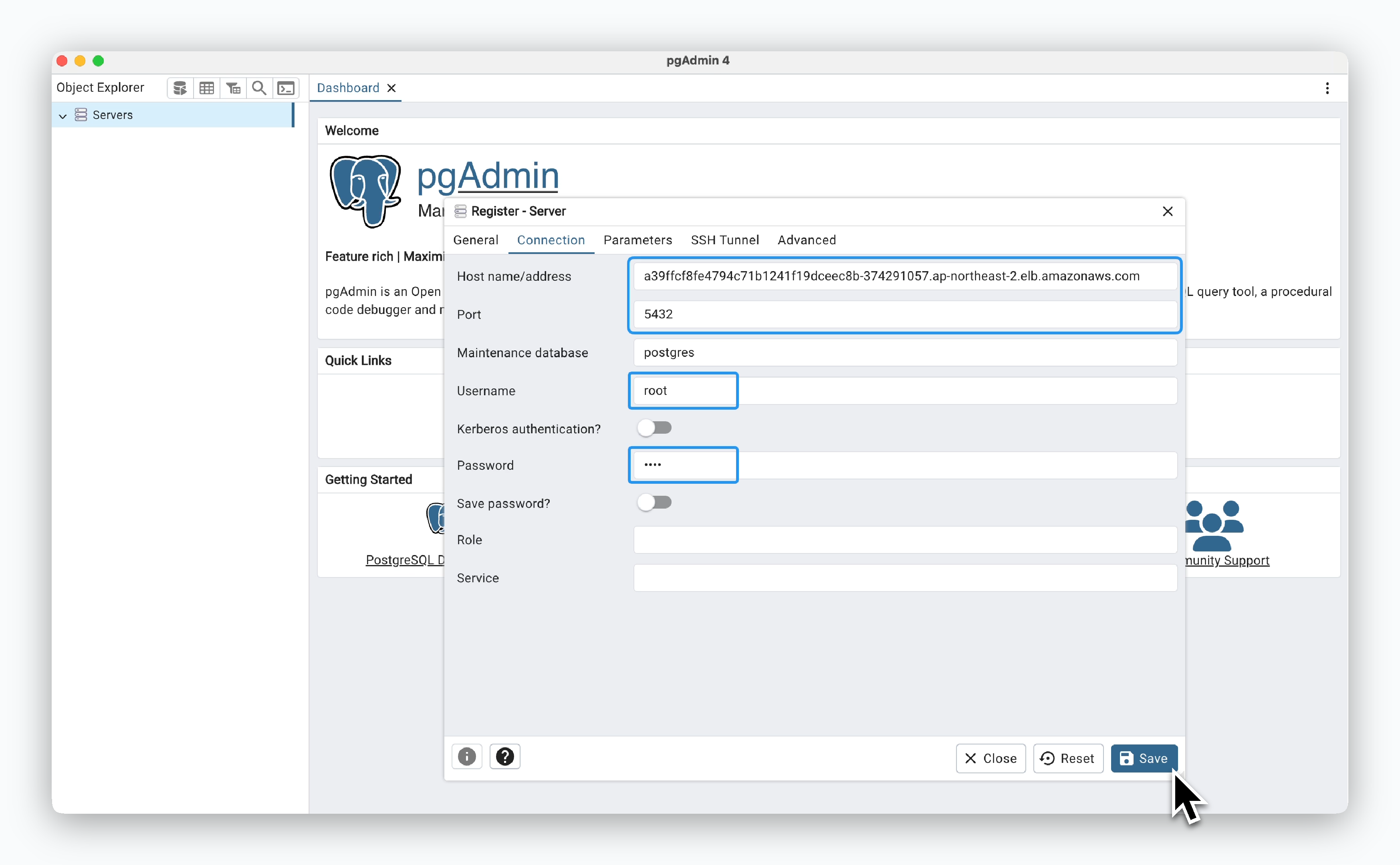
In the Connection tab, enter the ingress address, the Username (default is root), and the Root Password you set during deployment.
MongoDB - MongoDB Compass
MongoDB - MongoDB Compass
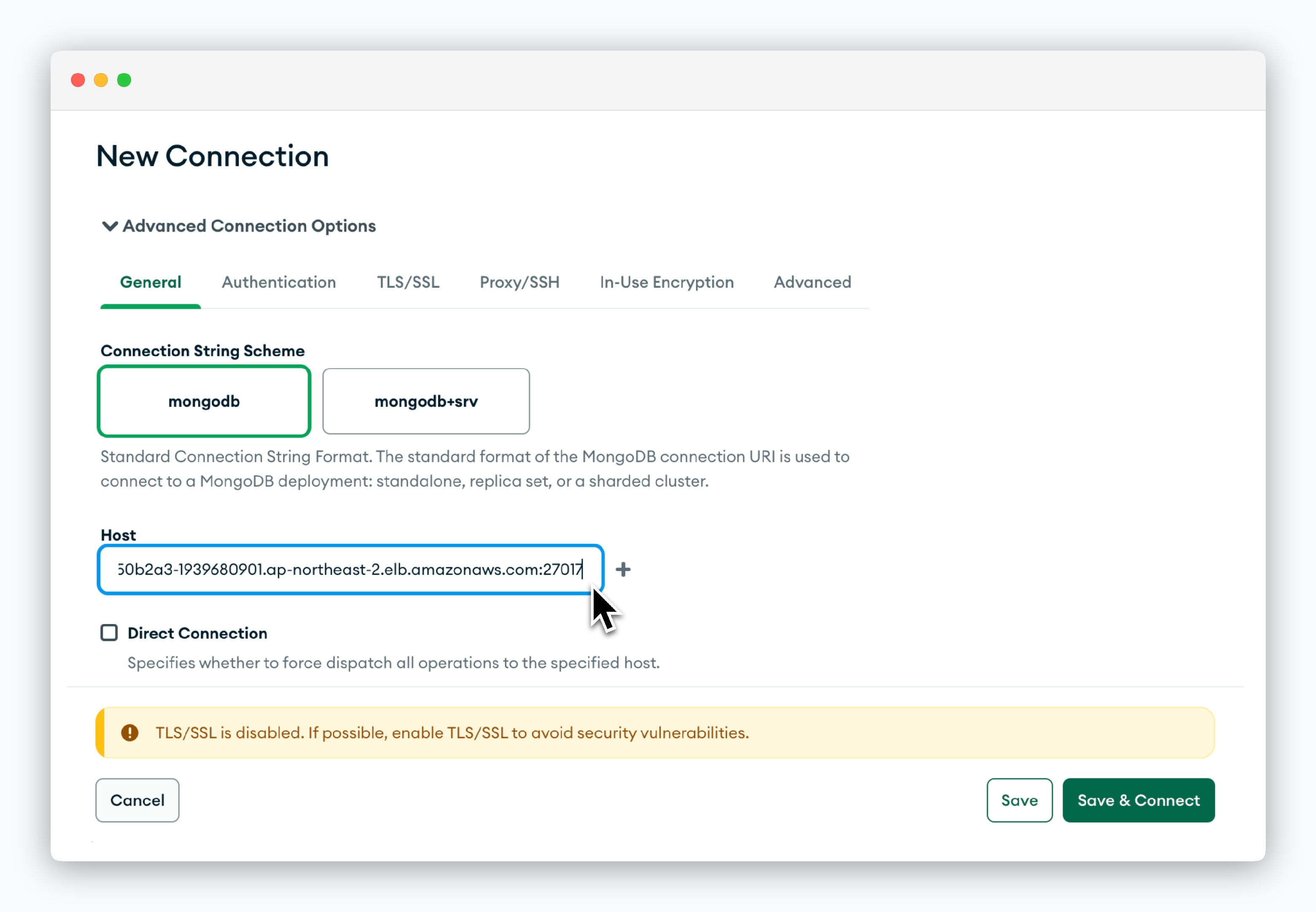
Click New Connection, then in the Advanced Connection Options section, enter the hostname including the port number in the Host field.
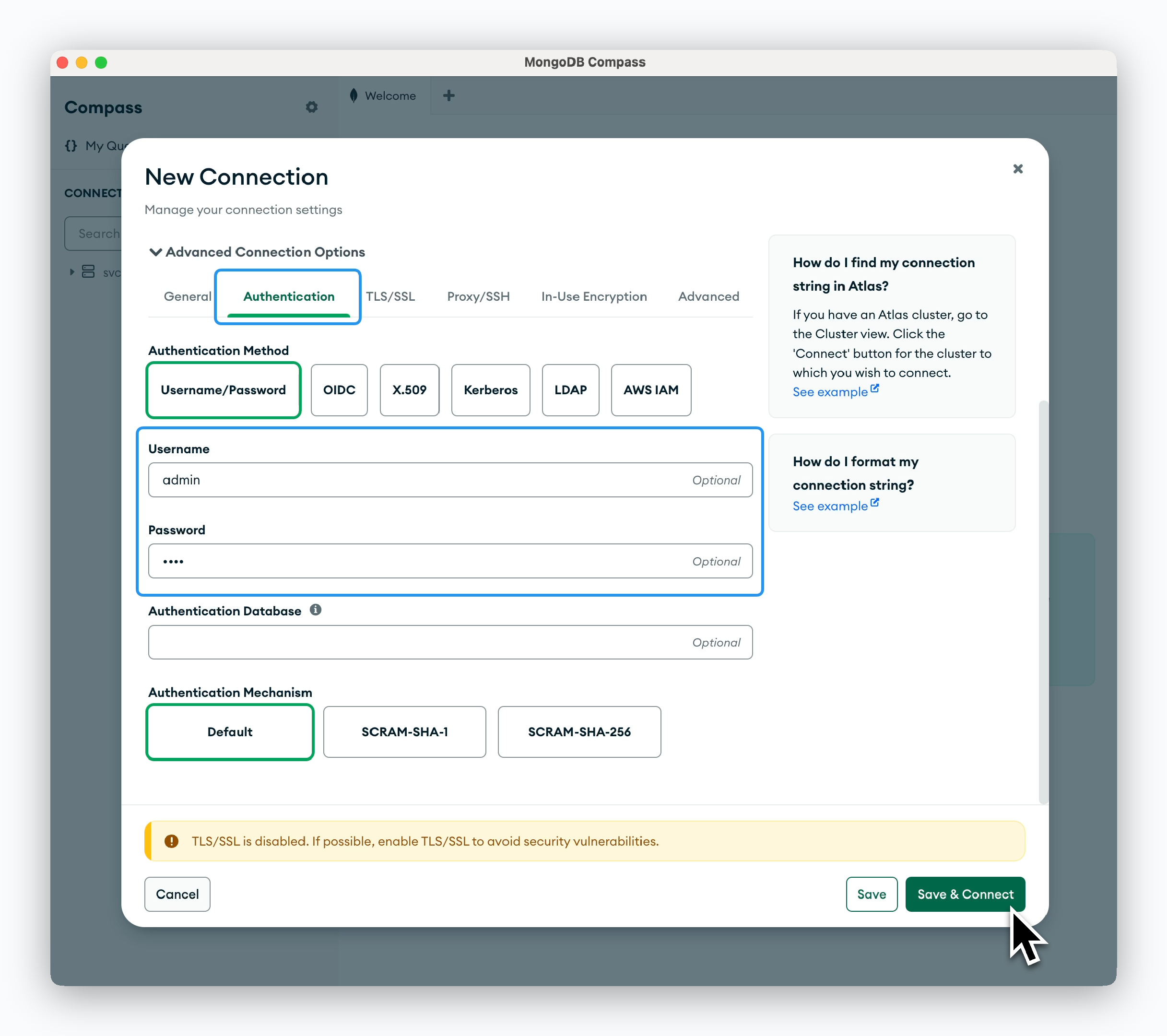
In the Authentication tab, enter the Username (default is admin) and the Root Password you set during deployment.
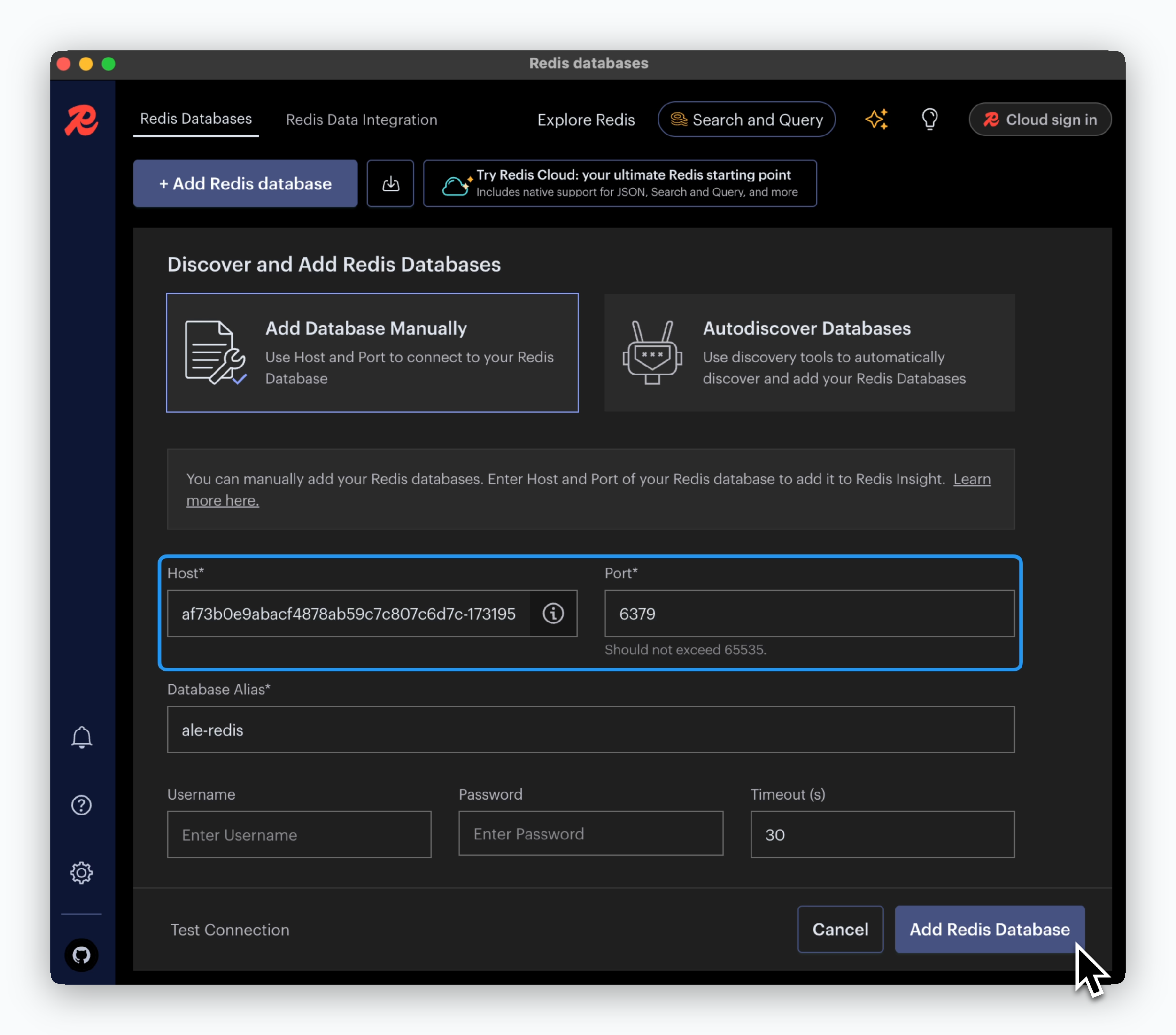
Redis - Redis Insight
Redis - Redis Insight
Database Management
Disk Space
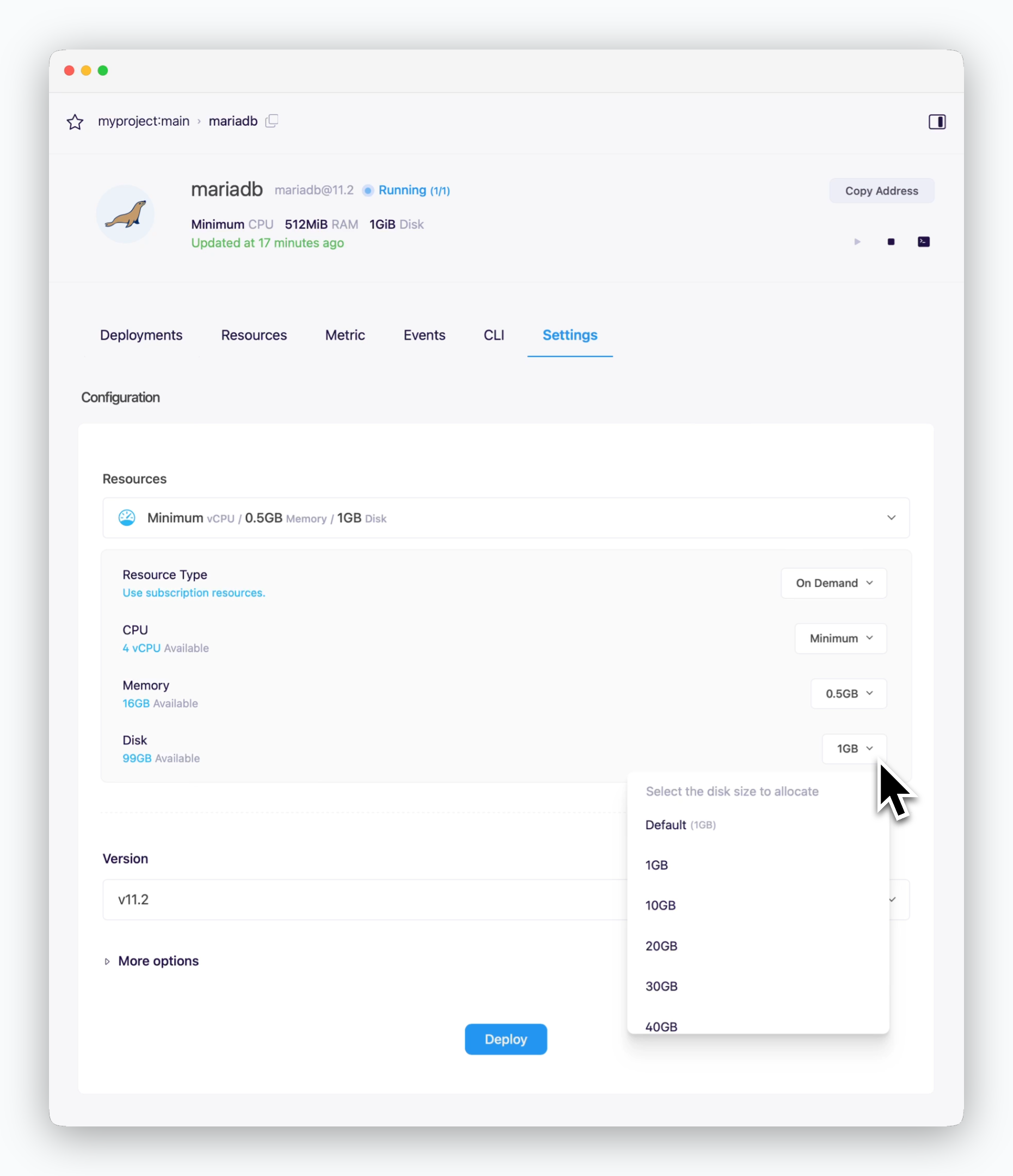
You can modify the Disk Resource in the Settings tab of the service page. Click Deploy to apply the new disk capacity.
When you deploy with new resource configurations, the disk capacity will be updated while preserving all existing data.
Root Password
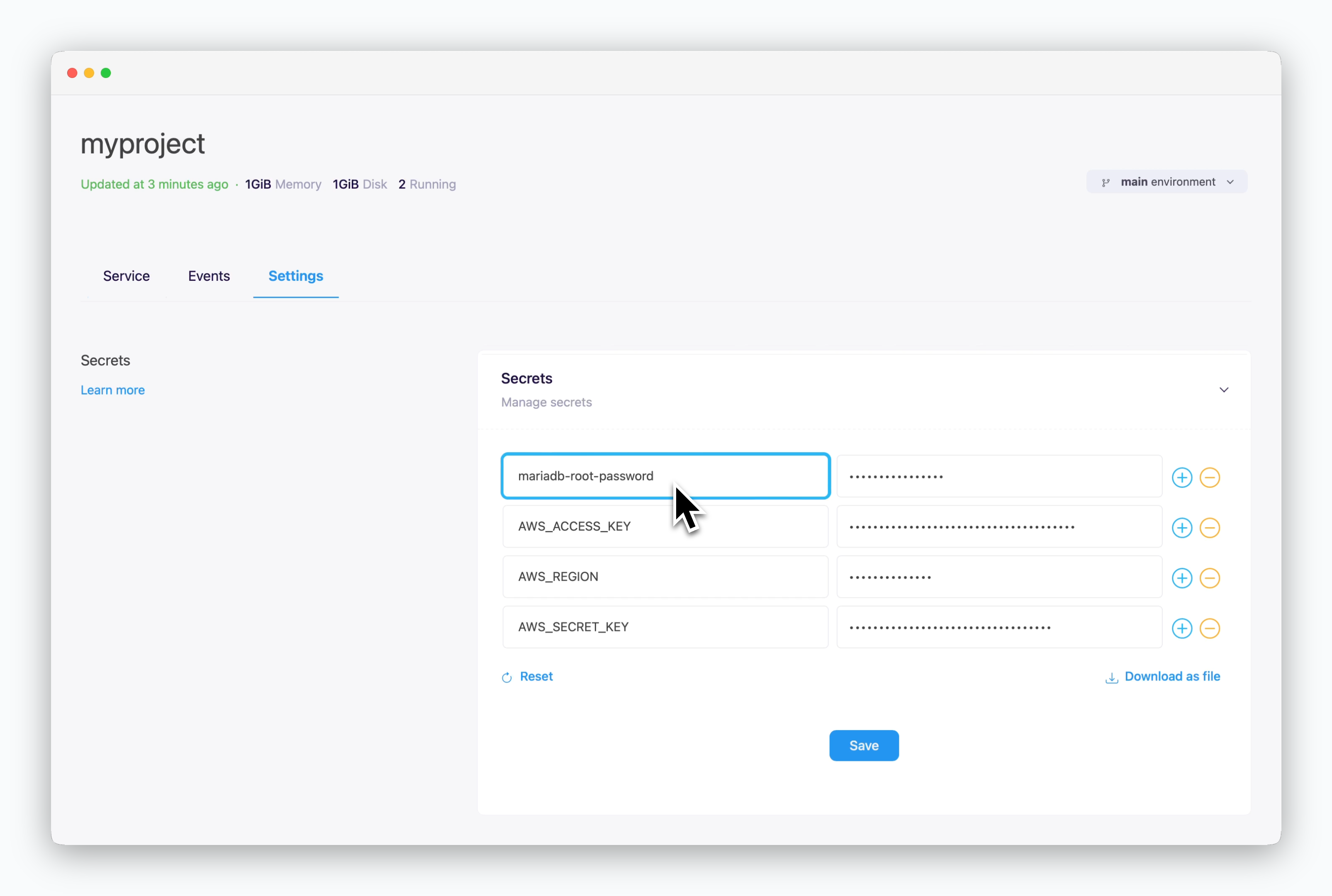
The Root Password can be viewed and managed in the Secrets section of environment settings.
Database Deletion
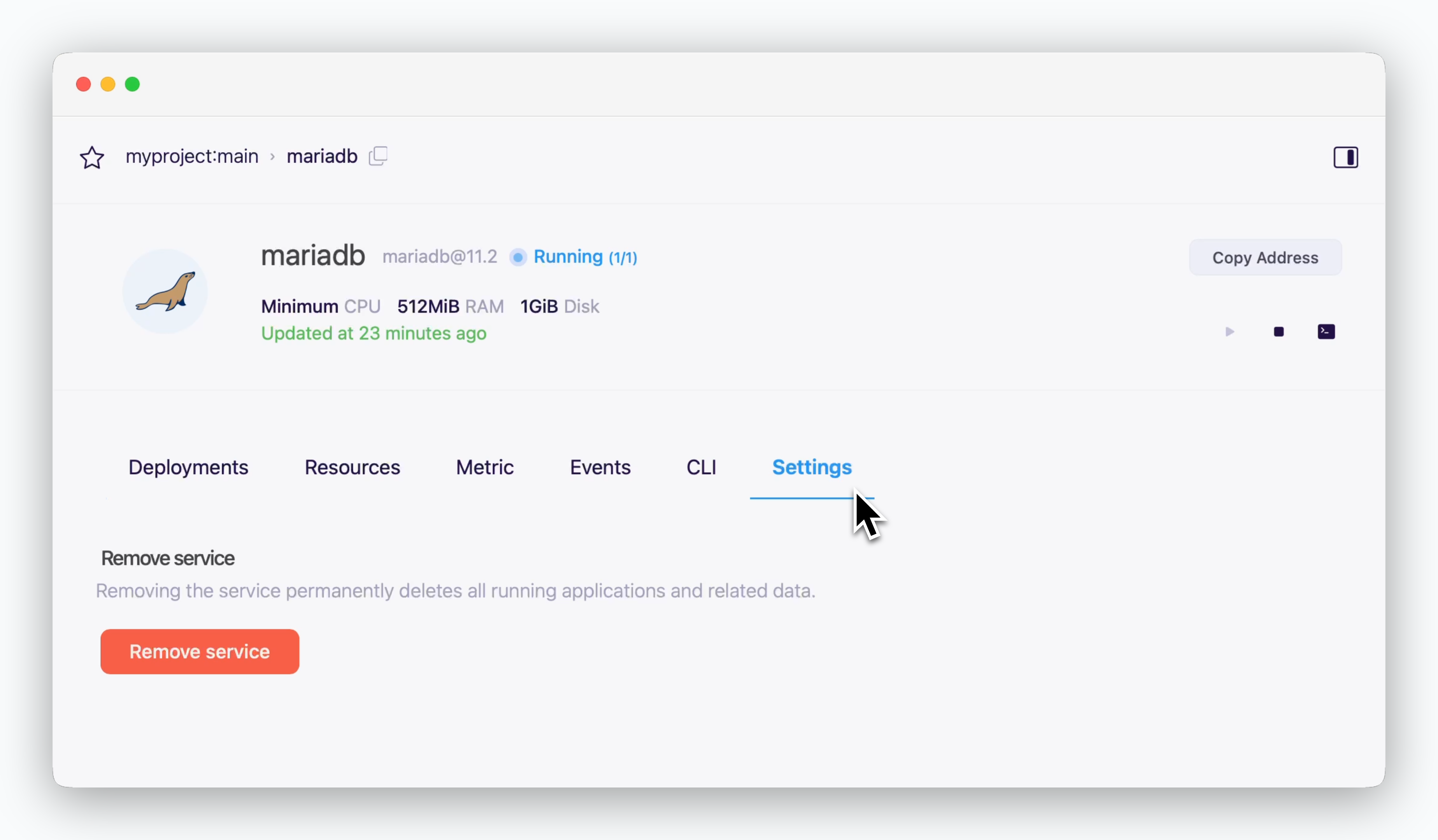
You can delete your database service by clicking Remove Service in the Settings tab of the service page.