Automate service deployments using GitHub Actions workflows that are automatically generated upon deployment.
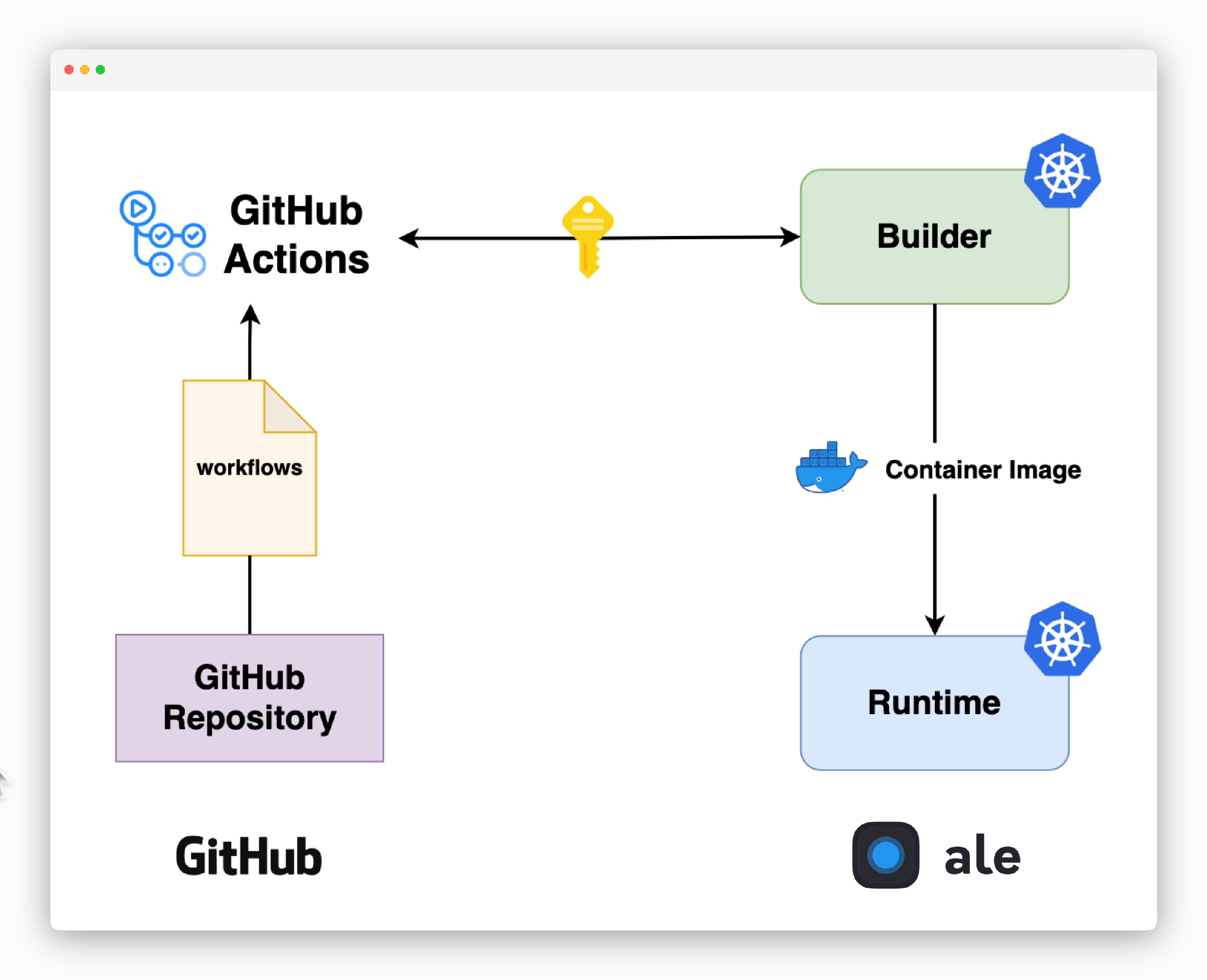
Credentials Setup
To enable communication between ale and GitHub, set up authentication credentials.
Generate GitHub Personal Access Token
Generate GitHub Personal Access Token
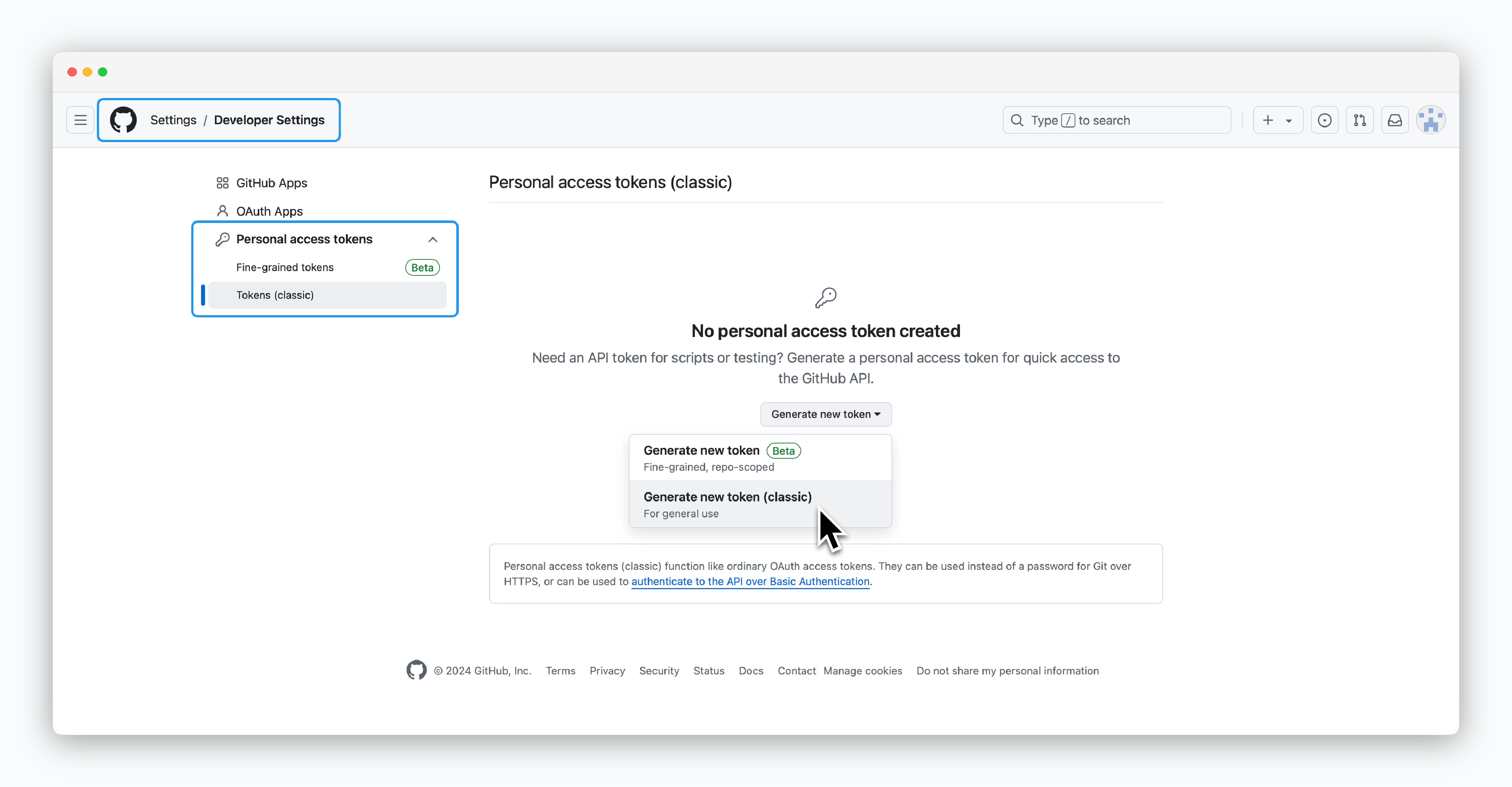
Go to Developer Settings in your GitHub account, select Personal access tokens from the sidebar, then click Generate new token (classic)
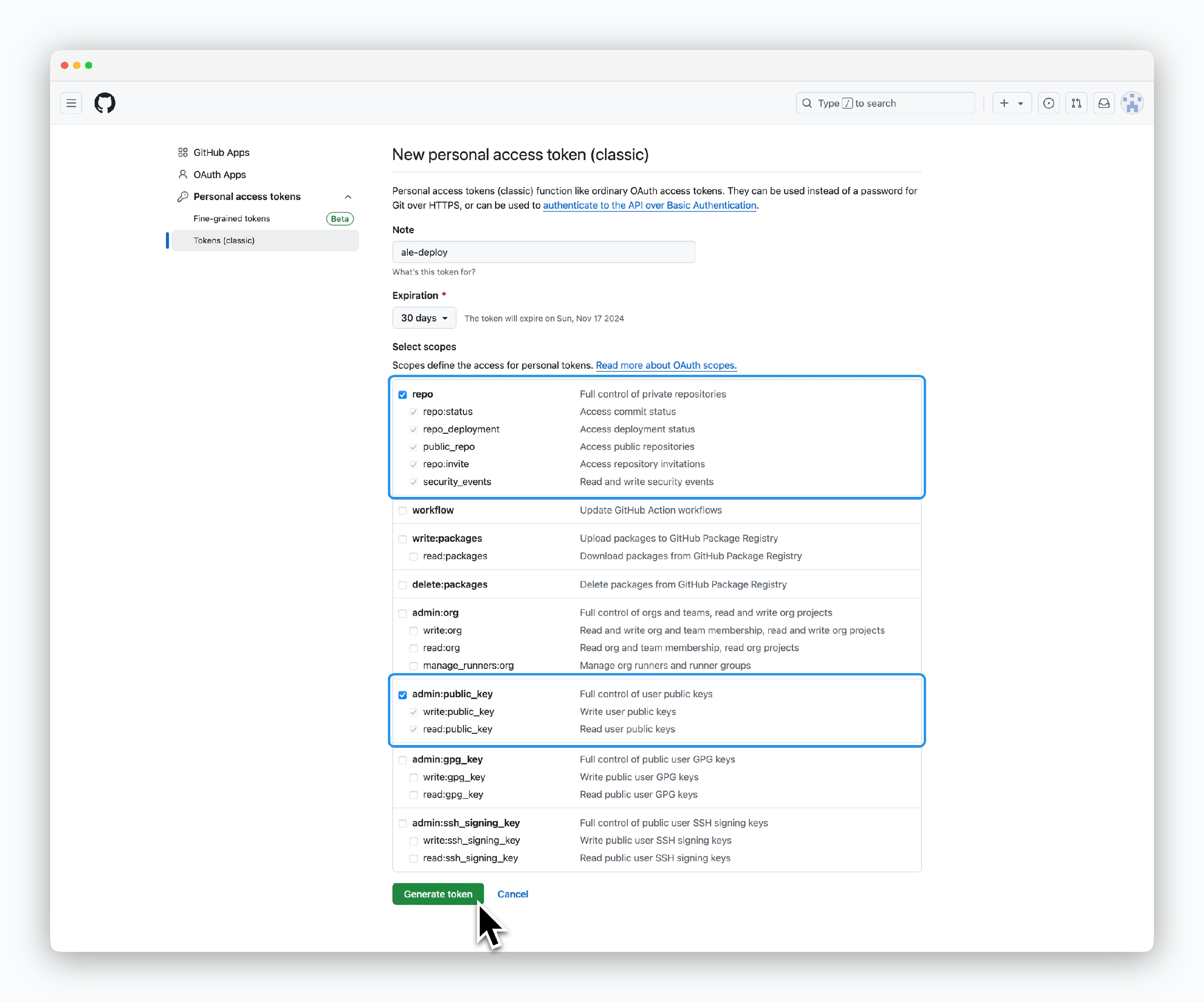
Select bothrepoandadmin:public_keyscopes, then clickGenerate token.
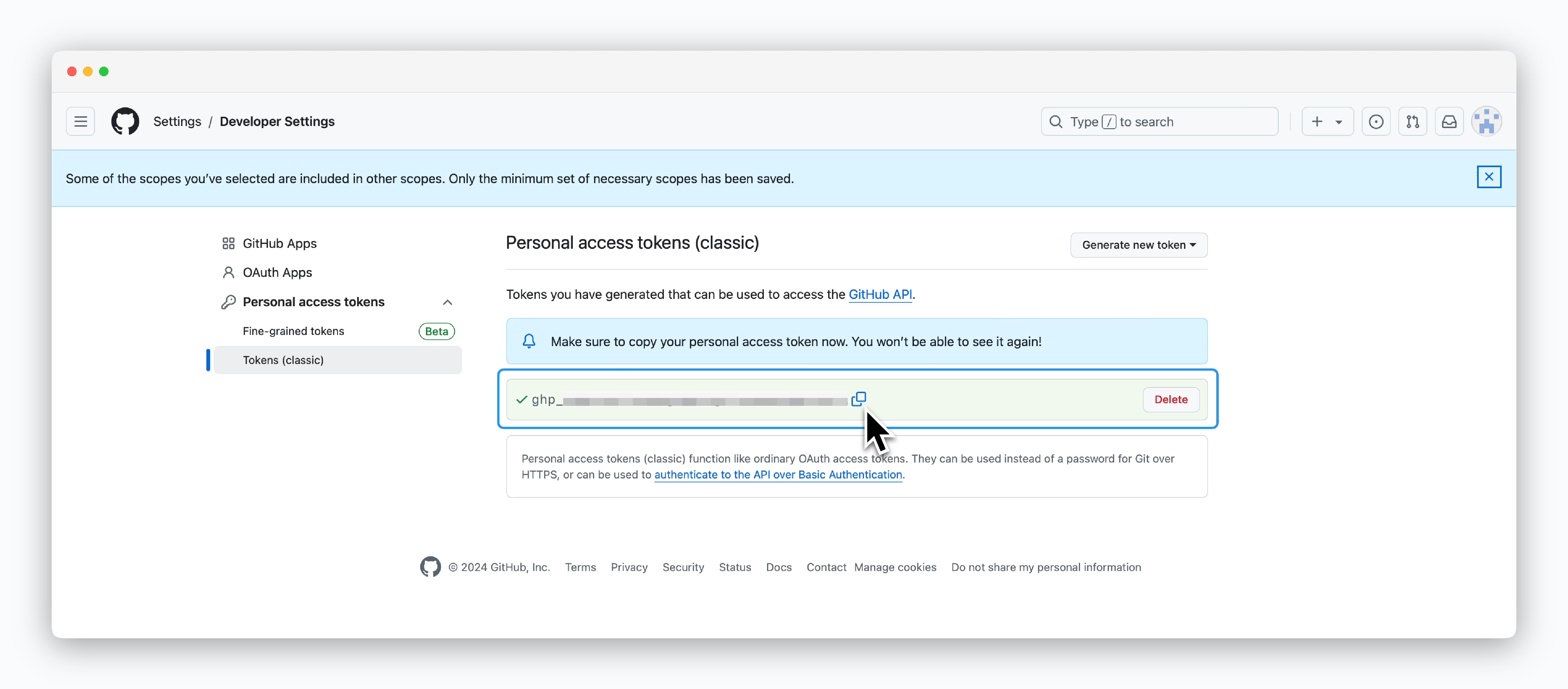
Copy and store the token.
Generate ale API Key
Generate ale API Key
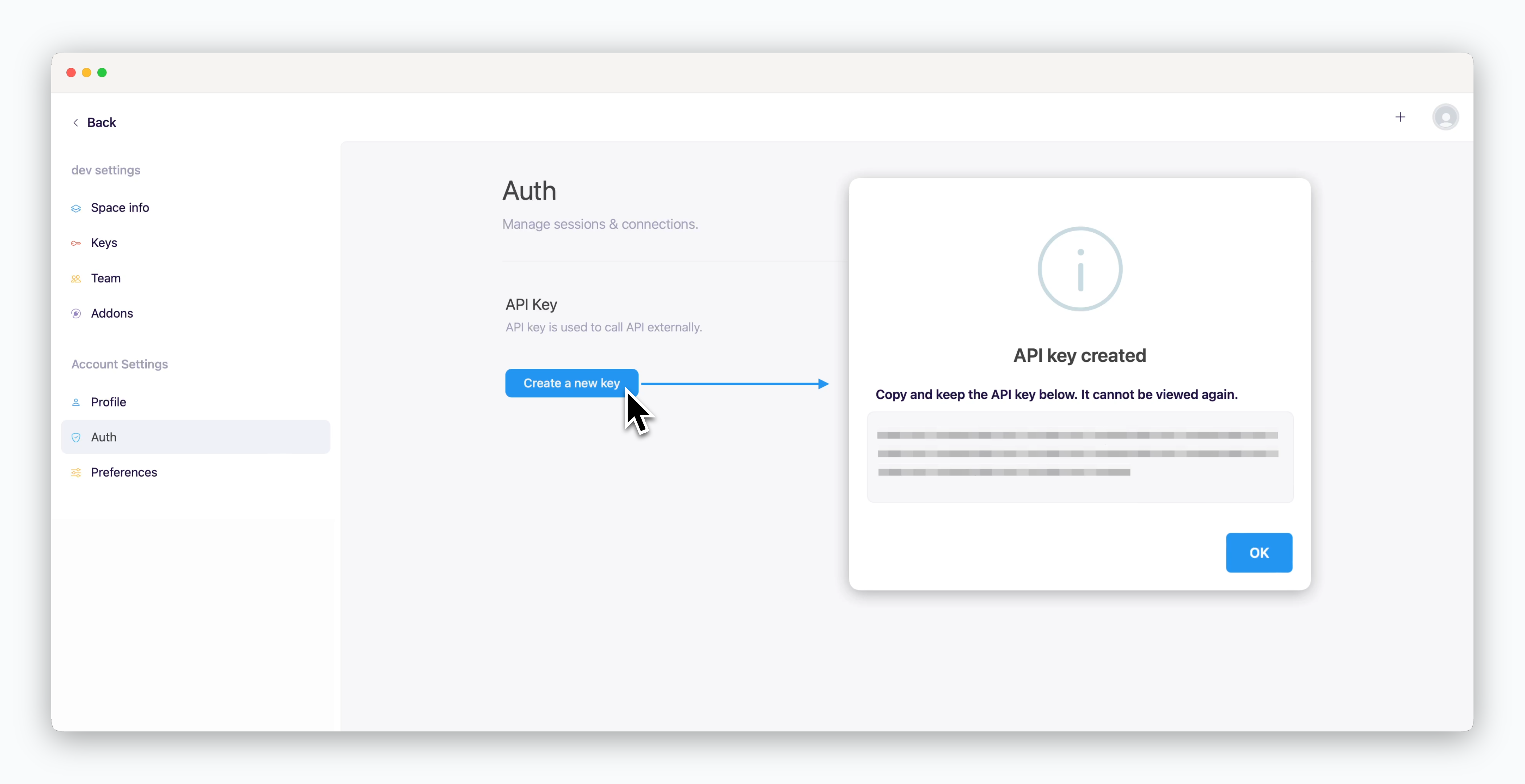
Inale, clickCreate a New Keyin the Auth page of your space settings.
Configure the Above Secrets as GitHub Actions Secrets
Configure the Above Secrets as GitHub Actions Secrets
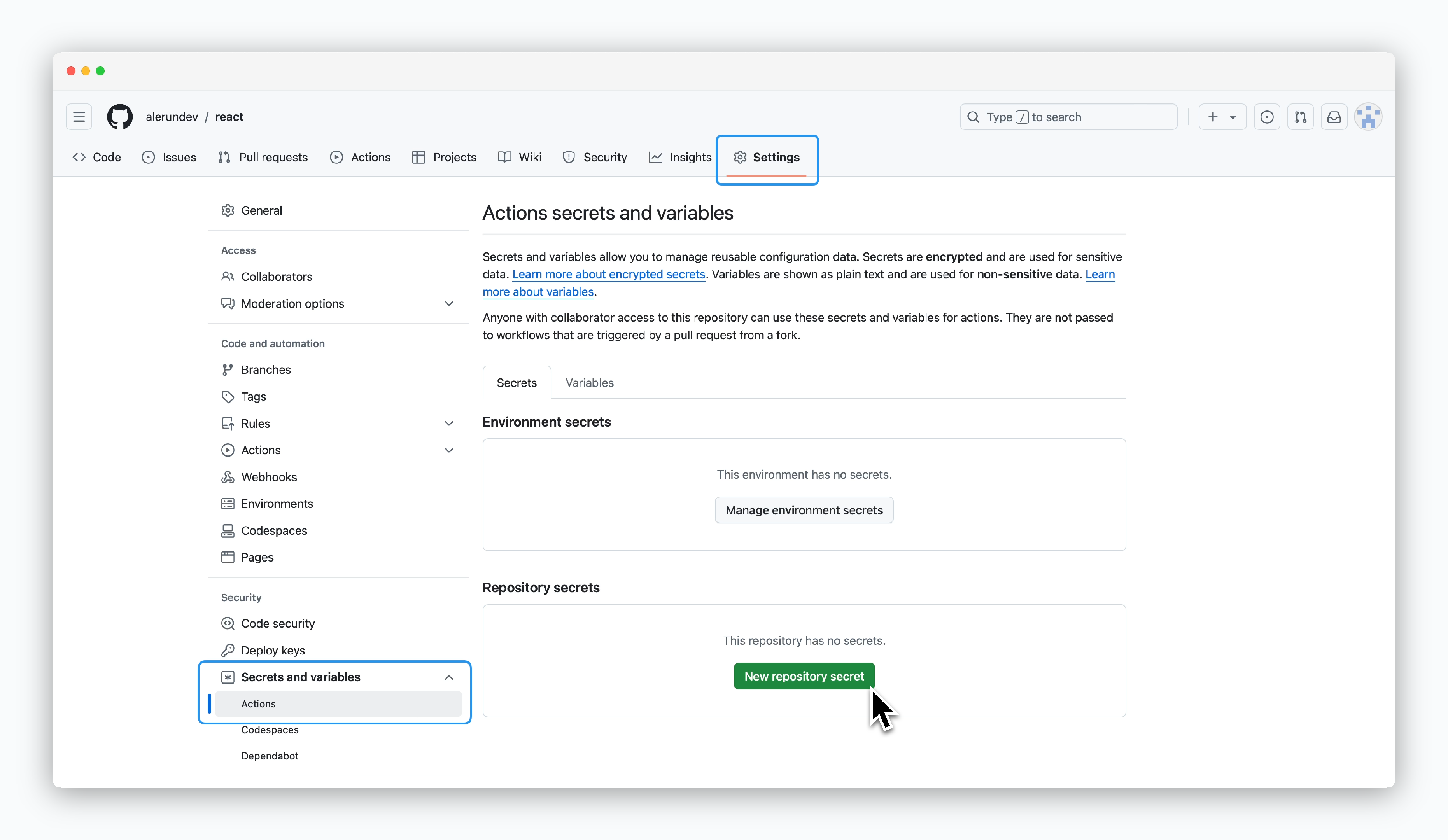
Go to Repository Settings > Secrets and variables > Actions, then click New repository secret.
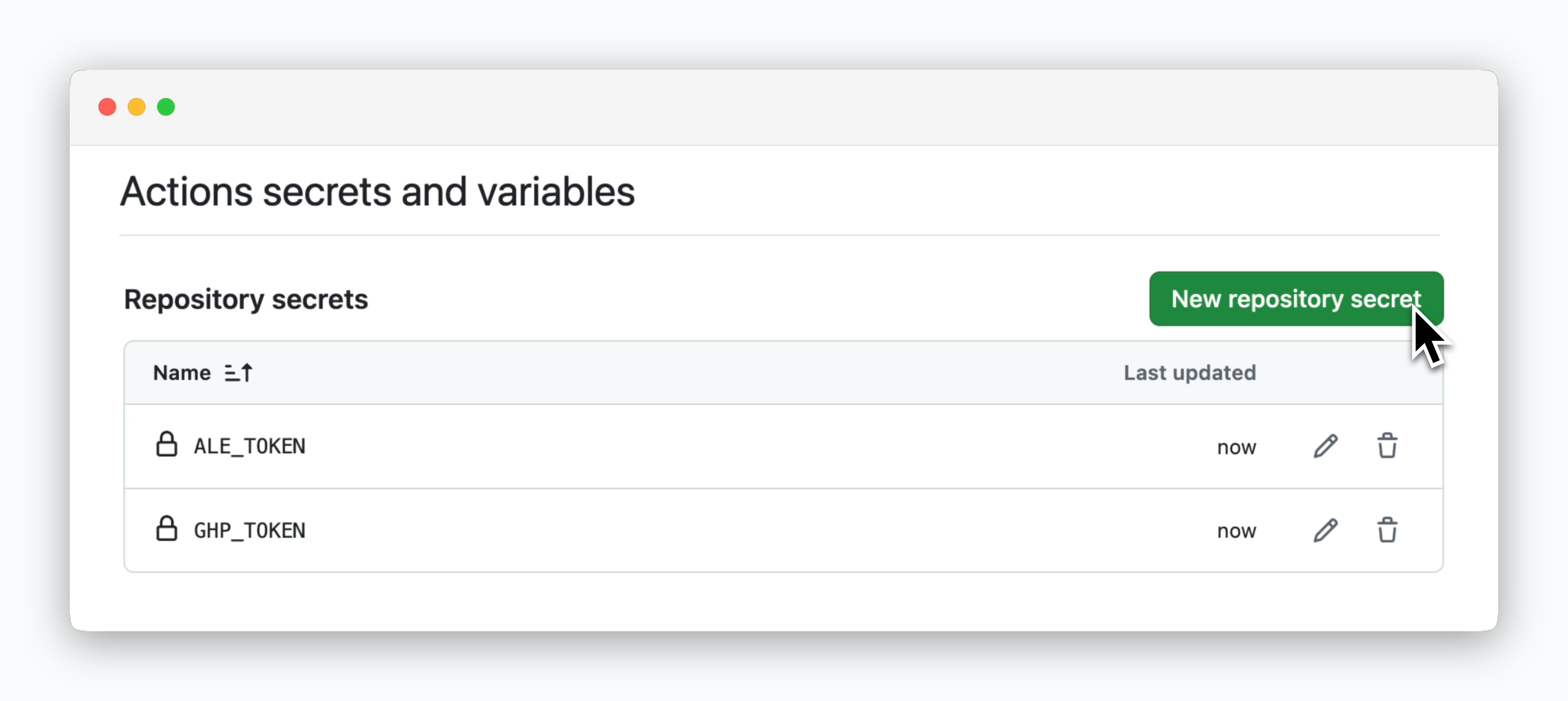
Add two repository secrets with the following values:
| Name | Secret |
|---|---|
| ALE_TOKEN | ale API key |
| GHP_TOKEN | GitHub Personal Access Token |
GitHub Actions Setup
Get Workflow Code
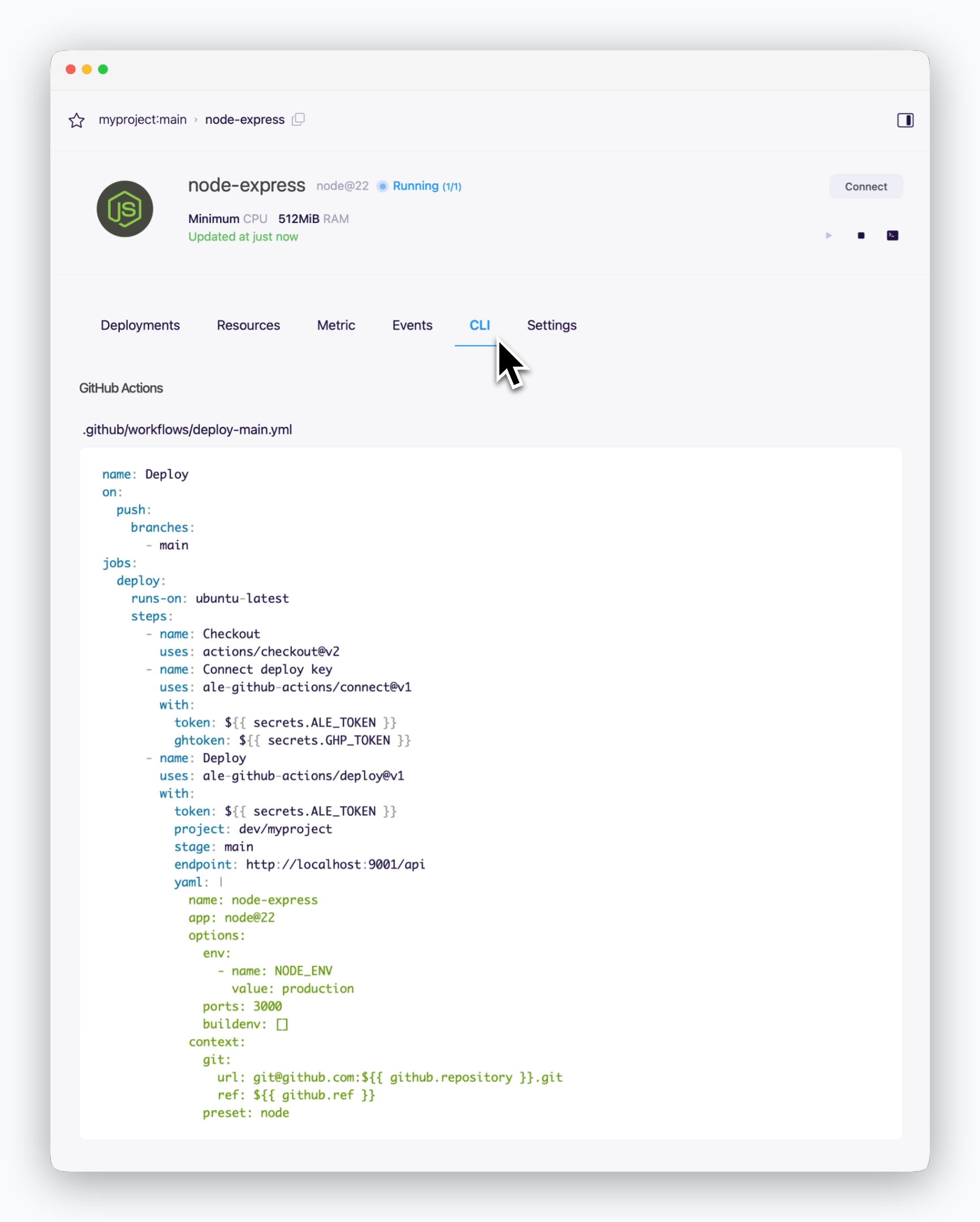
Navigate to the service page and copy the auto-generated GitHub Actions workflow code from the CLI tab.
The endpoint automatically changes depending on the environment where
ale is installed.Create Workflow File
Create a .github/workflows directory in your project’s root and add a yaml file using the code copied from ale.
The .github/workflows folder path is required and fixed, but you can choose any filename for your workflow.
Action Input Parameters
The pre-configured GitHub Actions workflow includes two main actions: the connect action, which configures GitHub repository Deploy Keys forale’s source access, and the deploy action, which sends deployment settings toaleand triggers the deployment process.
Connect Action Inputs
Connect Action Inputs
| Input | Description | Required / Default |
|---|---|---|
| token | ale API Key | Required |
| ghtoken | GitHub Personal Token | Required |
| endpoint | ale API Endpoint | Required (https://app.[domain]/api) |
| scope | Target space name | Default: API Key user’s space name |
| repo | GitHub repository (format: user/repo) | Default: Current action’s repository |
| readOnly | Generate read-only deploy key if set to ‘true’ | Default: false |
Deploy Action Inputs
Deploy Action Inputs
| Input | Description | Required / Default |
|---|---|---|
| token | ale API Key | Required |
| endpoint | ale API Endpoint | Required (https://app.[domain]/api) |
| project | Project name to deploy | Required (space/project) |
| stage | Deployment environment name | Default: Project’s default environment |
| allStages | Deploy to all environments if ‘true’ | Default: false |
| repo | GitHub repository (format: user/repo) | Default: Current action’s repository |
| file | Deployment config file location | Default: .cloudtype/app.yaml |
| json | Deployment config JSON text | - |
| yaml | Deployment config YAML text | - |
Advanced Usage
The generated workflow file can be customized to fit your service needs.
Subdirectory Configuration
Subdirectory Configuration
- Specify the deployment directory with the path field
Resource Configuration
Resource Configuration
By default, services use the resource configuration defined in ale. You can customize resource settings in the resources section of your YAML file
The spot field determines the VM type:
true for Spot, false for On-demand.Environment Variables
Environment Variables
Environment variables can be managed in two ways:
- Configure via dashboard (automatically synced to workflow)
- Define directly in YAML using the options.env array
Service Port Configuration
Service Port Configuration
Specify up to three service ports in the options.ports field using comma-separated values.