Guide for deploying generic Python applications.
Prerequisites
Supported Python Versions
Supported Python Versions
| Django Version | Supported Python Version |
|---|---|
| Django 3.1 | 3.6, 3.7, 3.8, 3.9 |
| Django 3.2 | 3.6, 3.7, 3.8, 3.9, 3.10 |
| Django 4.0 | 3.8, 3.9, 3.10 |
| Django 4.1 | 3.8, 3.9, 3.10, 3.11 |
| Django 4.2 | 3.8, 3.9, 3.10, 3.11, 3.12 |
| Django 5.0 | 3.10, 3.11, 3.12 |
| Django 5.1 | 3.10, 3.11, 3.12 |
Select Template and Repository
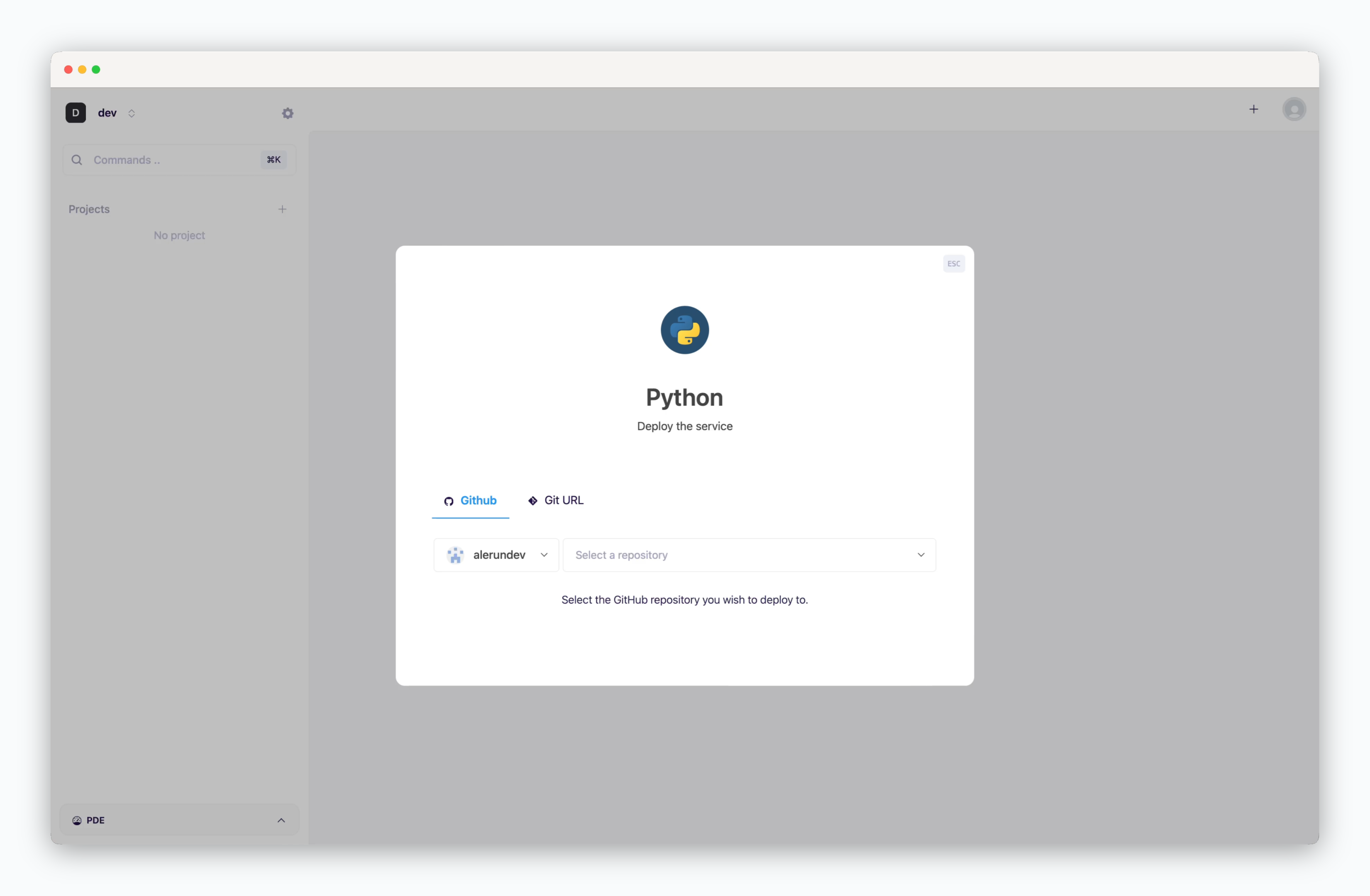
On the dashboard, click or ⌘ + K to open the deployment modal and select the Python template. Then choose a GitHub repository from the dropdown or input a Git repository URL in the Git URL tab.
Deployment Settings
Apply the following settings to ensure your service runs seamlessly.
Basic Settings
Basic Settings
- Version
- Environment Variables
- Port Number:
8000(default) - Start Command:
python3 manage.py runserver 0:8000(default) - Health Check: Endpoint for verifying container status
More Options
More Options
- Build Variables: Variables to include during container image builds
- Embedded node.js: Node.js version required for builds within the project
- Install Command: Python package installation command
- Pre-start Command: Commands to execute before the start command
- Update strategy
- Rolling Update: Deploy new version incrementally while maintaining service availability. Requires sufficient node resources
- Recreate: Stop all instances before deploying new version. Results in downtime
By setting environment variables and pre-start commands as follows, you can create a Super User:
Set Resources and Deploy
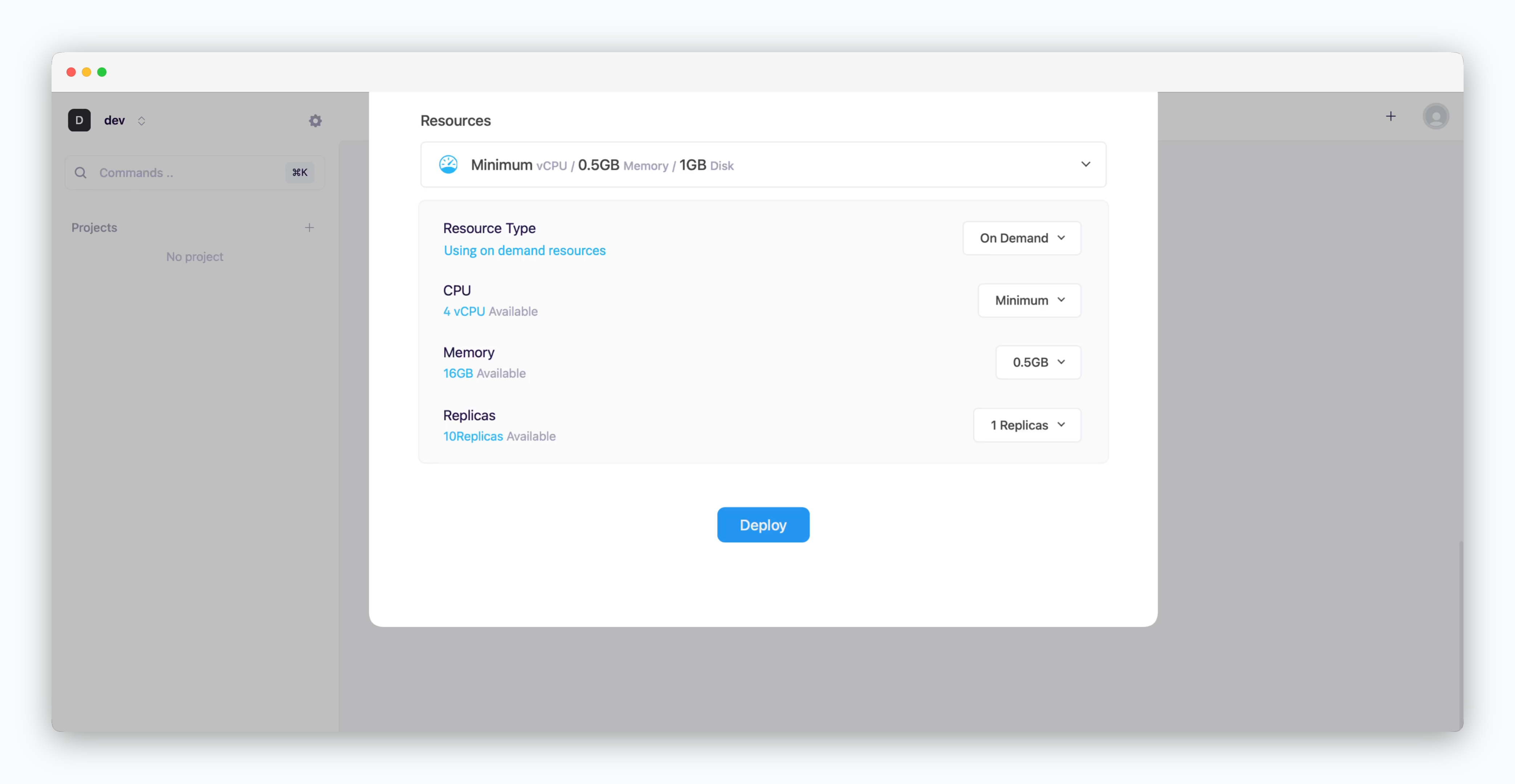
- Resource Type: Select between On-demand or Spot instance types
- CPU: Maximum vCPU resource for the service. Minimum vCPU means 0.1 vCPU
- Memory: Maximum memory size your service can use
- Replica: Number of service replicas for high availability and load balancing
-
Deploy: Click
Deploy
Once deployment is complete, you can access the web page via the preview domain or send requests using an API tool.
Django Docs